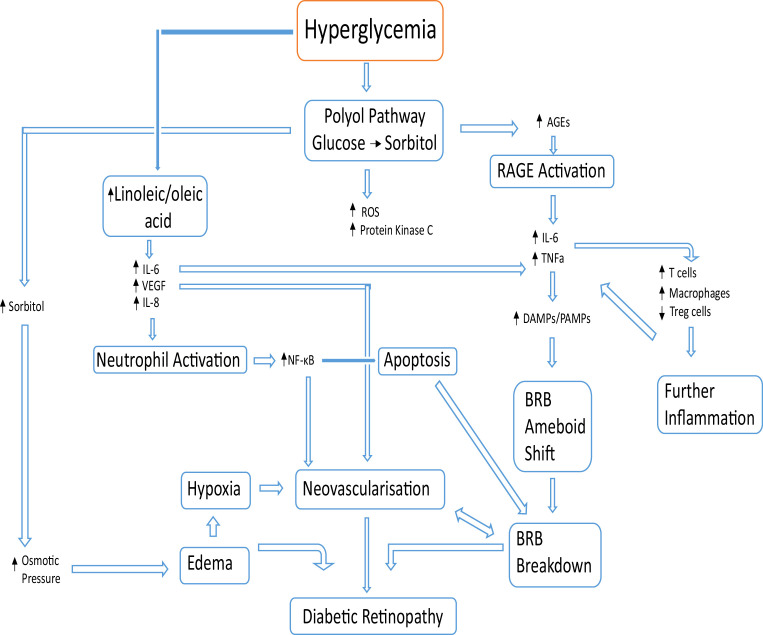
Figure 2.
Basic overview of pathological events leading to DR. Beginning with hyperglycemia, alternative glucose metabolic pathways create excess sorbitol and cytotoxic end products. The increase in advanced glycation end products results in more binding with the corresponding receptor (RAGE) causing an increase in proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8 and VEGF). An increase in linoleic and oleic acid increases the levels of IL-6, IL-8 and VEGF, which activate neutrophils. The blood retinal barrier breakdown is caused by apoptosis from neutrophil activation in conjunction with damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) activation causing a Blood Retinal Barrier (BRB) phenotype shift to a more ameboid state. DR results from BRB breakdown, local neovascularization and edema.