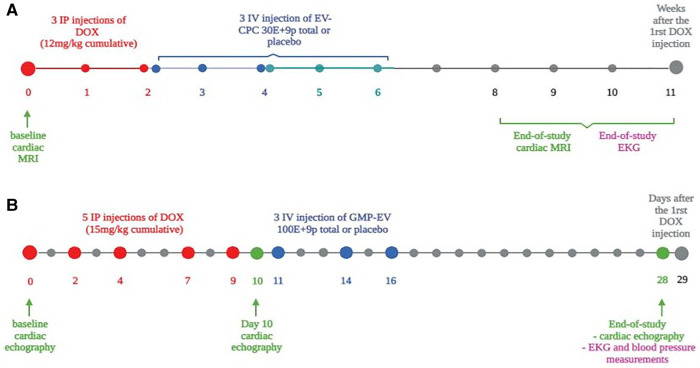
Figure 1.
Rodent CCM model experimental protocols. (A) Mice were subjected to 3 weekly intraperitoneal injections of doxorubicin (DOX) (cumulative dose = 12 mg/kg). Sham-operated mice underwent isotonic buffer injections without DOX treatment.Three equal doses of EV-CPC (total dose of 30E+9 particles) were given intravenously (IV) by the retro-orbital sinus (n = 30) according to 3 slightly different time frames: starting 15 days after the last Dox injection and performed every 4-5 days (one series) or every 3-4 days (one series) or starting the day after the last Dox injection and performed every 4-5 days (one series). A placebo control group underwent injections of isotonic buffer according to the same timing and delivery protocol. Cardiac MRI and EKG measurements were performed to assess cardiac function. Baseline values correspond to the functional measurements which were taken in 5 healthy mice at the onset of the protocol. (B) Wistar female rats received 5 IP injections of DOX (3mg/kg each; total cumulative dose 15mg/kg) followed by 3 intravenous injections of GMP-EV (100E+9/injection, one every 2/3 days; n = 12). Control rats were placebo-injected with saline (n = 11) or sham-treated (no DOX; n = 6). Cardiac echocardiography measurements were acquired at baseline before DOX treatment, between DOX and GMP-EV treatment at day 10 (D10), and 29 days after the first DOX injection (end-of-study). At this time, EKG and blood pressure measurements were also performed. Rats were sacrificed at end-of-study, 29 days after the beginning of DOX treatment. In order to avoid selection bias, DOX animals were randomized into the 2 different treatment groups relative to their clinical status, mostly their weight loss percentage compared to baseline. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; IP, intraperitoneal; IV, intravenous; EKG, electrocardiogram.