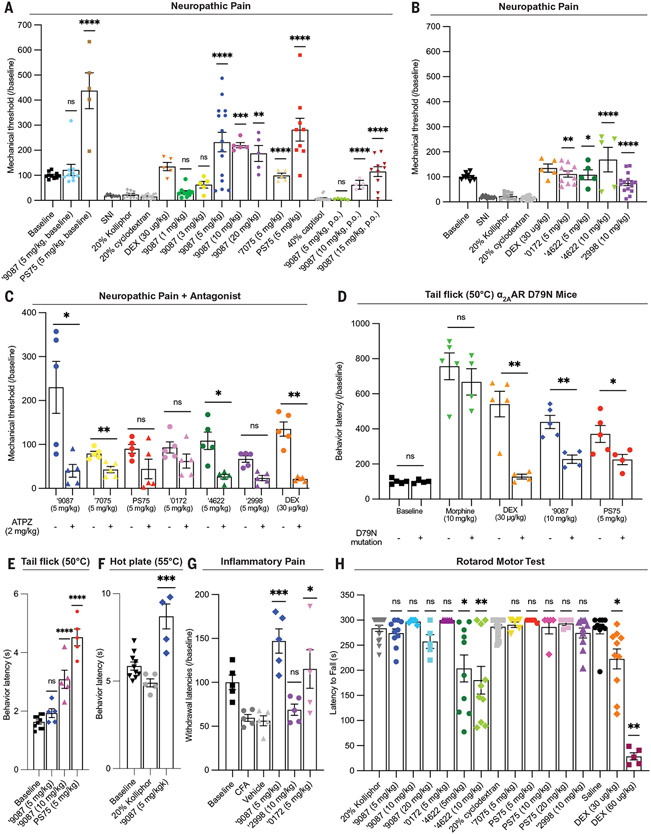
Fig. 4. The docking-derived agonists are antinociceptive in neuropathic, inflammatory, and acute thermal pain through the α2AAR but are not sedating.
(A to C) Effect of new α2AAR agonists in neuropathic pain model in mice after SNI with mechanical allodynia. (A) The new agonists ‘9087 and PS75 administered in naïve mice (baseline versus ‘9087, 5 mg/kg; baseline versus PS75, 5 mg/kg; one-way ANOVA; ns, not significant; ****P < 0.0001), dose response of ‘9087 in SNI mice and analogs ‘7075 and PS75 compared with their vehicles (20% kolliphor versus all ‘9087 doses; 20% cyclodextran versus ‘7075 and PS75; one-way ANOVA; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001) with positive control dexmedetomidine (DEX), and ‘9087 administered orally (p.o.) compared with its vehicle (40% captisol versus ‘9087 doses; one-way ANOVA; ****P < 0.0001). (B) Effect of additional agonists ‘4622, ‘0172, and ‘2998 compared with their vehicles (20% kolliphor versus ‘4622, 5 mg/kg; ‘4622, 10 mg/kg; and ‘0172, 5 mg/kg; one-way ANOVA; 20% cyclodextran versus ‘2998; two-tailed t test; ns = *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001) and positive control DEX. (C) Administration of α2AR antagonist atipamezole (ATPZ, 2 mg/kg i.p.) to block agonist efficacy in neuropathic pain model (‘9087 versus ‘9087 with ATPZ; ‘7075 versus ‘7075 with ATPZ; PS75 versus PS75 with ATPZ; ‘0172 versus ‘0172 with ATPZ; ‘4622 versus ‘4622 with ATPZ; ‘2998 versus ‘2998 with ATPZ; DEX versus DEX with ATPZ; two-tailed t test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (D) Diminished analgesia in α2AAR D79N mice in the 50°C tail flick assay for acute thermal (heat) pain. The mutation does not affect morphine analgesia but substantially decreases the analgesia by DEX, ‘9087, and PS75 (baseline WT versus D79N; morphine WT versus D79N; DEX WT versus D79N; ‘9087 WT versus D79N; PS75 WT versus D79N; two-tailed t test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (E) Analgesia of ‘9087 and PS75 in 50°C tail flick assay for acute thermal (heat) pain compared with its vehicle (20% Kolliphor versus ‘9087 and PS75; one-way ANOVA; ****P < 0.0001). (F) Analgesia of ‘9087 in 55°C hot plate assay for acute thermal (heat) pain compared with its vehicle (20% Kolliphor versus ‘9087; two-tailed t test; ***P < 0.001). (G) Efficacy of newly characterized agonists in CFA-induced hyperalgesia compared with the vehicle (vehicle versus ‘9087, ‘2998, and ‘0172; one-way ANOVA; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001). (H) Evaluating motor impairment and sedation of newly characterized agonists in the rotarod motor test. Only ‘4622 causes slight motor impairment, whereas other agonists do not. DEX causes significant impairment and complete sedation at higher doses. All compounds compared with their vehicles (20% Kolliphor versus ‘9087, ‘0172, and ‘4622; 20% cyclodextran versus ‘2298, ‘7075, and PS75; saline versus DEX; one-way ANOVA; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001). For (A) to (G), all compounds were administered s.c., unless otherwise indicated. Data are shown as individual data points and means ± SEMs (n = 4to 25).