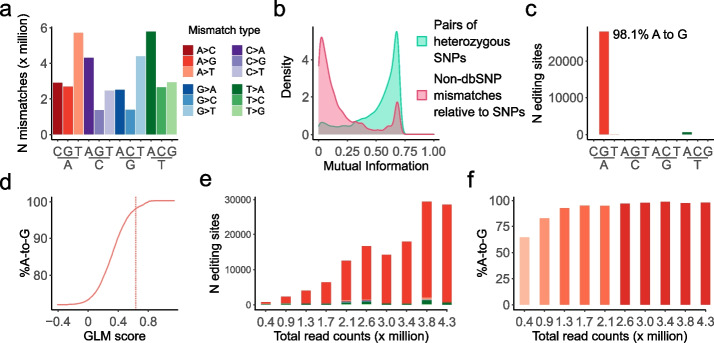
Fig. 2.
Identification of RNA editing sites in long-read RNA-seq data of the brain sample of an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patient. a Raw mismatches detected in the dataset. b Mutual information for pairs of putative heterozygous SNPs (based on dbSNP) or non-dbSNP mismatches relative to putative SNPs. c RNA editing sites identified by L-GIREMI. d %A-to-G among all predicted editing sites vs. GLM score. Dotted line denotes the score cutoff used for c (0.64). e Number of RNA editing sites identified given different read coverages (randomly chosen subsets of the AD dataset). f %A-to-G among the RNA editing sites identified in the subsets in e