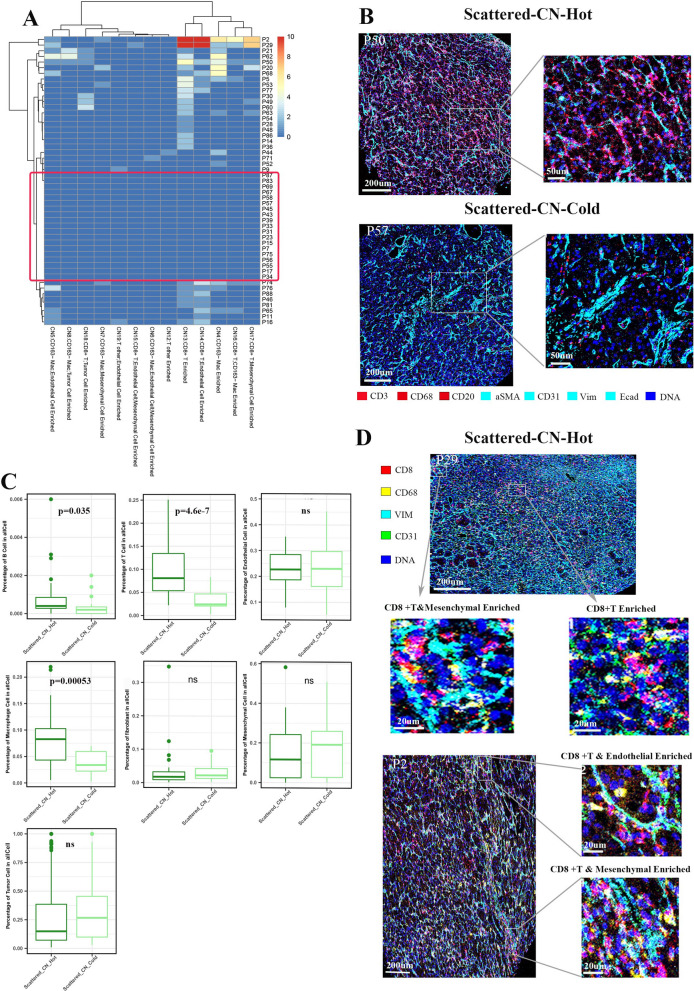
Fig. 6.
Scattered group can be divided into immune-cold and -hot phenotypes. A Unsupervised clustering of the ccRCC tissues with scattered immune architecture. Red box reflects the immune-cold phenotype. Scale bar represents the number of CNs, with a maximum limit of 10. B Spatial relationship between the immune (CD3, CD20 and CD68) and non-immune (αSMA, CD31, Vim and Ecad) components in the scattered-CN-cold and scattered-CN-hot phenotypes. C Comparison of the proportion of different cell types between the scattered-CN-cold and scattered-CN-hot phenotypes. D Representative IMC images of the scattered-CN-hot phenotype (P2 and P29). The zoomed areas display the characteristic CNs within the ccRCC tissues