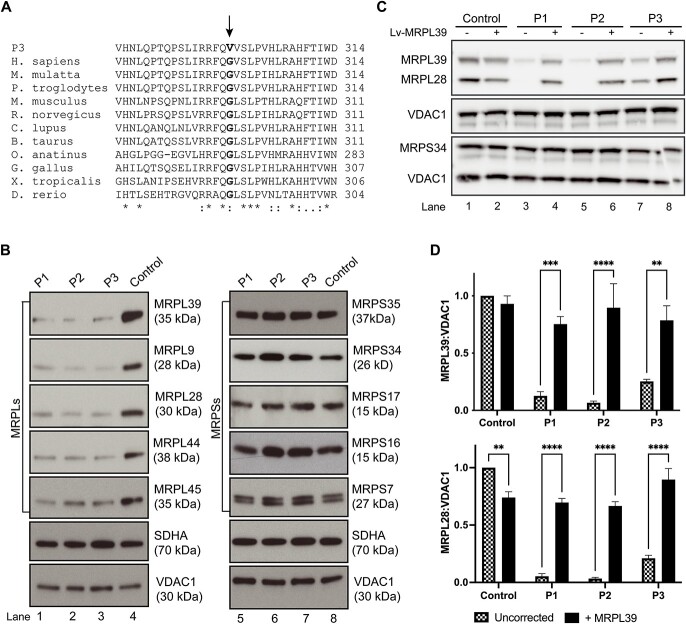
Figure 4.
The p.(Gly299Val) variant identified in individual P3 changes a highly conserved amino acid residue and results in selective destabilization of the mitochondrial large ribosomal subunit, in agreement with results seen in individuals P1 and P2. (A) Protein sequence alignment of MRPL39 with 11 of its homologs including Homo sapiens and 10 other vertebrate species. Asterisks (*) depict conserved amino acids and colons (:) depict semi-conserved residues. The p.Gly299 residue is changed to a valine in individual P3 and is indicated in bold and is 100% conserved in vertebrate species from humans to Danio rerio. (B) Representative immunoblots of large (MRPL) and small (MRPS) mitoribosomal proteins extracted from fibroblasts revealed a substantial decrease in MRPL levels in all three affected individuals including in MRPL39, whereas the MRPS levels remained comparable to controls. SDHA and VDAC1 represent loading controls for mitochondrial content. (C) Fibroblasts from a control individual and P1, P2 and P3 were transduced with wild-type MRPL39 cDNA. Representative SDS-PAGE immunoblot demonstrates an increase in protein levels of large mitoribosomal protein subunits, MRPL39 and MRPL28, in transduced patient fibroblasts relative to untransduced cells, whereas the small mitoribosomal protein subunit MRPS34 was unchanged. VDAC1 was used as a loading control. (D) Densitometry analysis revealed that the increase after transduction was significant in each patient. Results were normalized to VDAC1 and presented as the percent of average untransduced control cells. The data shown are the mean of three independent transfections ± SEM. **p < 0.002, ***p< 0.0002, ****p < 0.0001.