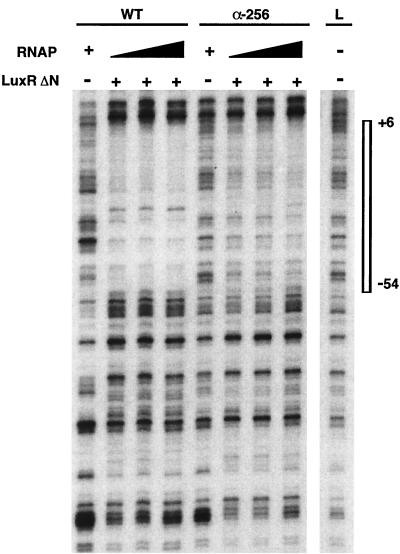
FIG. 3.
DNase I protection analysis of the luxI promoter (luxI coding strand) by RNAP with α-subunit C-terminal deletions. All lanes contained the γ-32P-labeled 325-bp EcoRI-PstI fragment of the regulatory DNA from pAMS103. The various RNAPs used are designated at the top as follows: WT, wild-type RNAP; α-256, mutant RNAP. DNase I cleavage patterns in the presence of RNAP only, as indicated by plus signs, are shown for both wild-type (20 nM) and α-256 (40 nM) RNAPs. Assays were also done with a range of RNAP concentrations, as indicated by the filled triangles (WT, 10, 20, and 40 nM; α-256, 20, 40, and 80 nM), in the presence of LuxRΔN. Addition of LuxRΔN (5 μM) is indicated by plus signs. The DNase I cleavage pattern for the DNA template is shown in lane L, with the lux box and the luxI −10 promoter region protected by the proteins (positions +6 to −54 in relation to the transcriptional start site) highlighted by the box to the right. Reactions were performed as previously described (23), with two minor modifications; i.e., the reaction volume was reduced from 60 to 30 μl, and the acetylated bovine serum albumin concentration was reduced from 2 to 0.1 mg/ml.