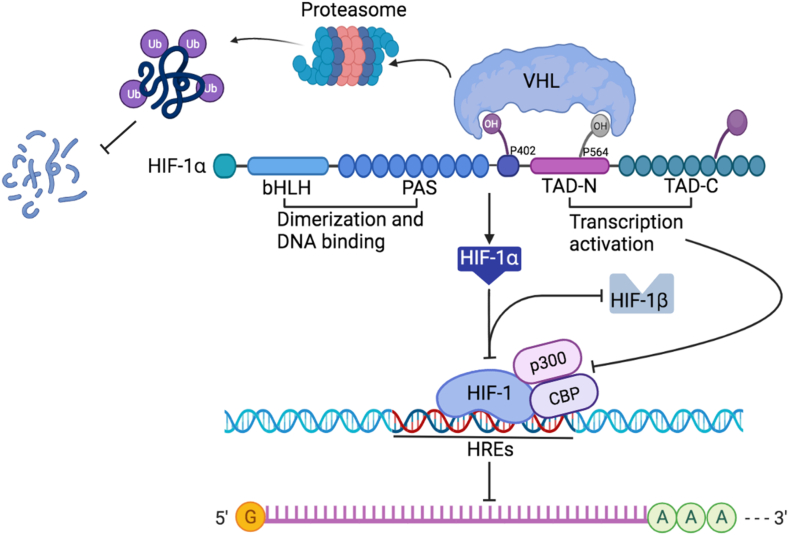
Fig. 1.
Structure and regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) stability. The stability of HIF-1α is regulated via proline hydroxylation modulated by prolyl hydroxylase domains (PHDs). Activated PHDs hydroxylate HIF-1α at its oxygen dependent degradation domain (ODDD), triggering its association with von hippel-lindau (VHL) protein E3 ligase complex and leading to ubiquitin–proteasome pathway-dependent degradation. Hypoxia increases protein stability of HIF-1α and promotes its nuclear translocation and accumulation. HIF-1α associates with transcriptional co-activators, such as cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB) binding protein (CBP) and p300; the efficient transcriptional complexes form in hypoxia response elements (HREs) to regulate gene expression.