Fig. 2. Lifetime suppresses intensity noise and improves fidelity of sub-threshold recording.
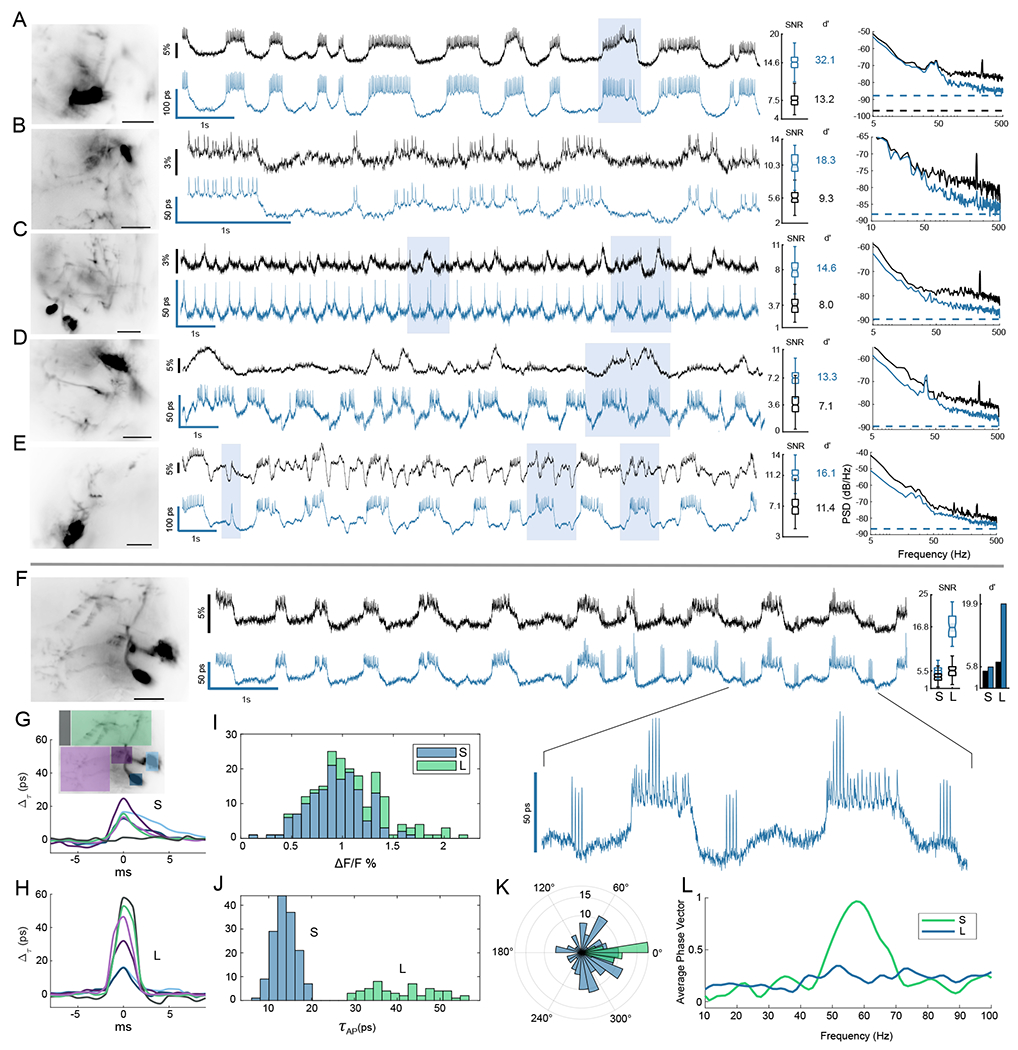
Six example MBON neurons are shown comparing lifetime (blue) to ΔF/F intensity recordings (black). Recordings were obtained by averaging over high-resolution images shown at left (scalebar 25 μm). Shaded boxes highlight some notable regions of the traces for improved lifetime readout. For each example, the distributions of spike SNR are compared for intensity and lifetime, with calculated spike detection fidelity d′ indicated. (A,B) Two examples of flies without motion demonstrate improvement of technical noise floor at high frequencies by up to 7 dB. The noise power spectra for the traces are compared at right, with dotted lines indicating the photon shot noise limits (C-E) Three examples of flies having low-frequency noise associated with motion artifacts. Lifetime improves noise power spectrum across temporal frequencies, rejecting intensity noise by up to 9 dB at low frequencies. See also further analysis in Fig. 3. (F-J) Lifetime provided an improved readout of two spike amplitudes in response to mechanical stimulus at 60 Hz. Large (L) spikes showed an enhanced lifetime responsivity and tripled detection SNR and d′ over the small (S) spikes. L spikes occured independent of sub-threshold waveform level but synchronized with spiking on plateaus in the inset. (G,H) Average spike waveforms for color-coded regions. The point of initiation for S spikes was a central region of the axon (consistent with Movies S1 and S2), while L spikes were diffuse and associated with background fluorescence. L spikes also correspond to local spikes in the dendrite and soma in (H). L spike background component possibly resulted from out of focus neurons (Movies S8 and S9). (I,J) Histograms of action potential amplitudes are compared. In intensity the L and S populations were not resolved and strongly overlap, but they were clearly separated in lifetime. Using lifetime to identify the spikes, the intensity histogram (I) is shaded with two colors to show overlapping populations. (K) A polar histogram demonstrates strong phase locking of the L spikes to mechanical stimulus using a bandpass filtered lifetime trace as phase reference. S spikes do not show phase locking. (L) The average phase vector length Σi cos(θi)/NAP is plotted vs. bandpass center frequency to show narrow-band locking response.
