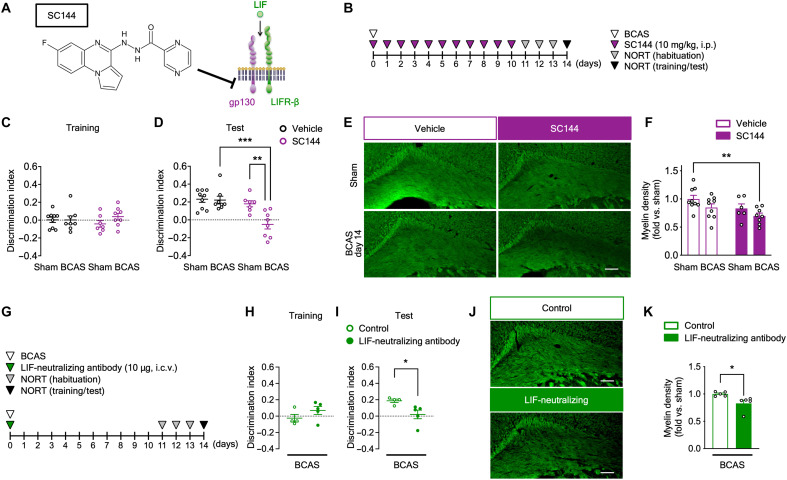
Fig. 7. Inhibition of LIF signaling accelerates BCAS-induced cognitive impairment and white matter injury.
(A) A schematic of the inhibitory mechanism of SC144. (B and G) The experimental time course for SC144 (B) or LIF-neutralizing antibody (G) administration and the NORT. (C, D, H, and I) Discrimination indexes for exploring the blue quadrangular object during the training session (C) and (H) and the wooden ball, i.e., novel object, during the test session (D) and (I) on postoperative day 14. (E, F, J, and K) Representative images of myelin staining in the corpus callosum (E) and (J) and summarized data for relative myelin density (F) and (K) on postoperative day 14. Values are means ± SEM. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) and (D) n = 7 to 9; (F) n = 6 to 9; (H) and (I) n = 4 to 5; (K) n = 5. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 for two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (D). **P < 0.01 for two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test (F). *P < 0.05 for two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (I). *P < 0.05 for two-tailed unpaired Welch’s t test (K). i.c.v., intracerebroventricular administration.