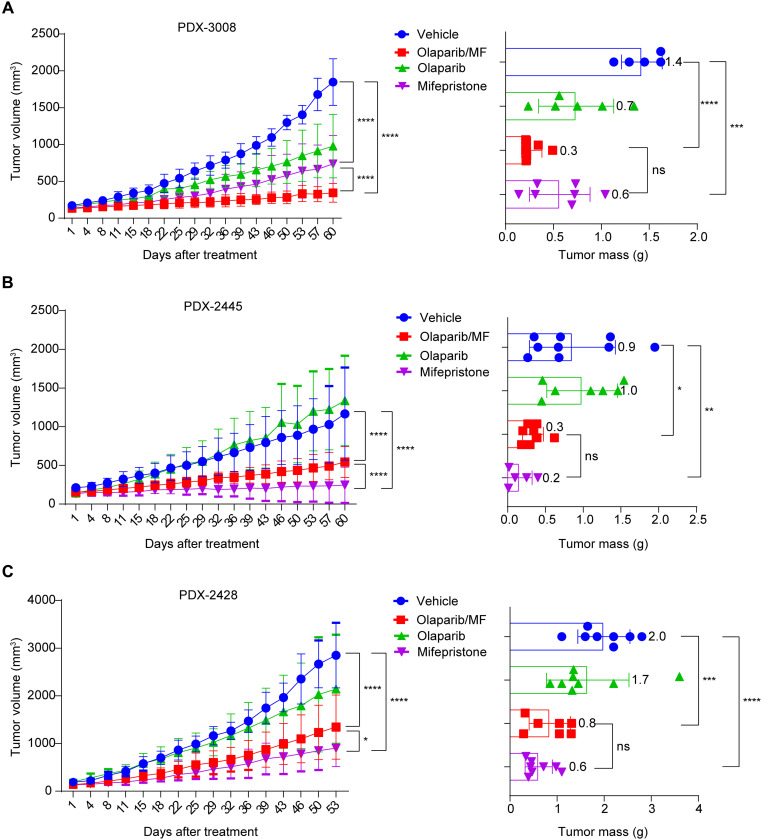
Fig. 7. Mifepristone mitigates tumor growth in ovarian HGSC PDX models.
(A) Ovarian HGSC PDX-3008 xenografts (BRCAWT, olaparib-naive tumors) were treated with olaparib (n = 6), mifepristone (n = 7), vehicle (n = 5), or olaparib in combination with mifepristone (n = 7) for 60 days. The left shows the mean tumor volume in the xenograft-bearing mice at the indicated times; the right shows the tumor mass after 60 days of treatment. Mifepristone monotherapy and mifepristone/olaparib treatment significantly suppressed tumor growth compared with vehicle (two-way ANOVA, ****P < 0.0001). Tumors treated with mifepristone alone (Welch’s t test, ***P = 0.0002) and those treated with mifepristone/olaparib (****P < 0.0001) had significantly smaller masses at harvest than did vehicle-treated tumors. Error bars indicate SD. (B) Olaparib-resistant BRCAWT ovarian HGSC PDX-2445 xenografts were treated with olaparib (n = 7), mifepristone (n = 5), vehicle (n = 9), or mifepristone/olaparib (n = 8) for 60 days. Both mifepristone monotherapy (two-way ANOVA, ****P < 0.0001) and mifepristone/olaparib combination therapy (****P < 0.0001) significantly suppressed tumor growth compared with vehicle treatment. Tumors treated with mifepristone monotherapy (Welch’s t test, **P = 0.0061) and mifepristone/olaparib combination therapy (*P = 0.0257) had significantly smaller masses at harvest (60 days after treatment) than did vehicle-treated tumors. Error bars indicate SD. (C) Olaparib-resistant BRCAWT ovarian HGSC PDX-2428 xenografts were treated with olaparib (n = 8), mifepristone (n = 8), vehicle (n = 8), or mifepristone/olaparib (n = 7) for 53 days. Both mifepristone monotherapy (two-way ANOVA, ****P < 0.0001) and mifepristone/olaparib combination treatment (****P < 0.0001) significantly suppressed tumor growth compared with vehicle treatment. Tumors treated with mifepristone monotherapy (Welch’s t test, ****P < 0.0001) and mifepristone/olaparib combination therapy (***P = 0.0006) had significantly smaller masses at harvest than did vehicle-treated tumors. Error bars indicate SD. ns, not significant.