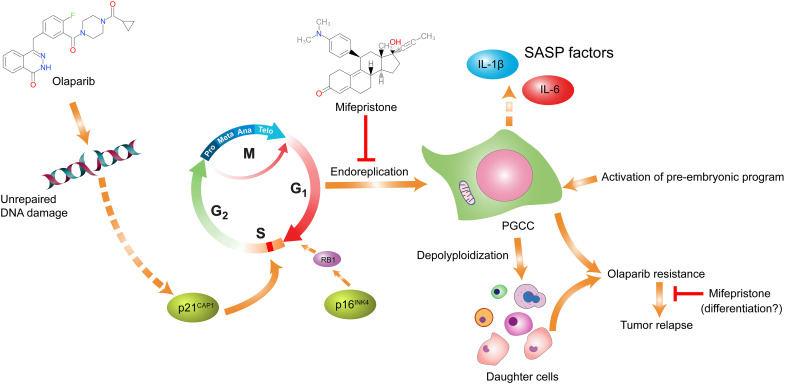
Fig. 8. Schematic model on how mifepristone potentiates olaparib-induced therapeutic response and blocks acquired resistance to PARPi in ovarian cancer.
Continuous exposure to olaparib results in unrepaired DNA damage, causing the activation of the aberrant endoreplication cell cycle. Cells that undergo endoreplication develop into senescent PGCCs, which give rise to daughter cells via a variety of modes of depolyploidization. The daughter cells acquired resistance via the life cycle of PGCCs and escaped senescence, eventually leading to tumor recurrence. The combined use of mifepristone and olaparib could block the development of PGCCs, thereby suppressing tumor growth. In tumors with acquired resistance, mifepristone can directly attenuate tumor growth, possibly by inducing differentiation toward benign lineages.