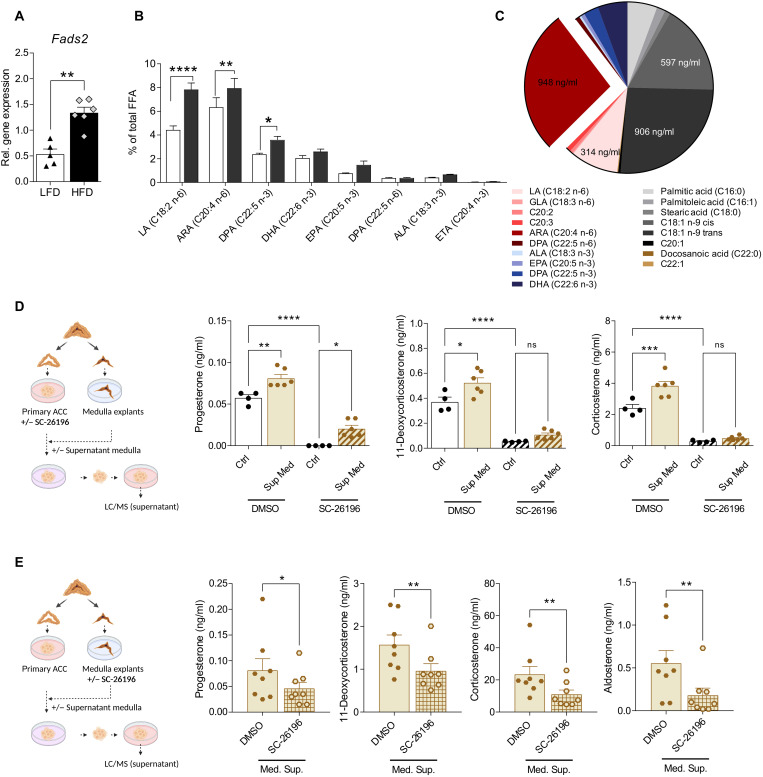
Fig. 3. Medulla-derived PUFAs promote adrenocortical steroidogenesis.
(A) Relative Fads2 expression in the adrenal medulla of mice fed for 20 weeks a LFD or HFD (n = 5 to 6 mice per group). Tbp was used as a housekeeping gene. (B) FFA were measured in the adrenal medulla of mice fed for 20 weeks a LFD or HFD by HPLC-MS (n = 3 mice per group). Results are presented as % of total FFA. (C) FFA measured in the supernatants of adrenal medulla explants kept for 18 hours in 100 μl of medium. Results are presented as % of total FFAs (n = 4). (D) Adrenocortical cells were treated for 6 hours with SC-26196 (10 μM) or DMSO and then received medulla explant–conditioned or control medium for another 18 hours. Steroids were measured in the adrenocortical cell supernatant by LC-MS/MS (n = 4 to 6). (E) Adrenal medulla explants were treated for 6 hours with SC-26196 (10 μM) or DMSO, washed thoroughly, and left another 18 hours in culture. Their supernatant was then applied on adrenocortical cell cultures, and 8 hours later, adrenocortical cell supernatants were collected and analyzed by LC-MS/MS (n = 8). Data in (A), (B), (D), and (E) are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. ns, not significant.