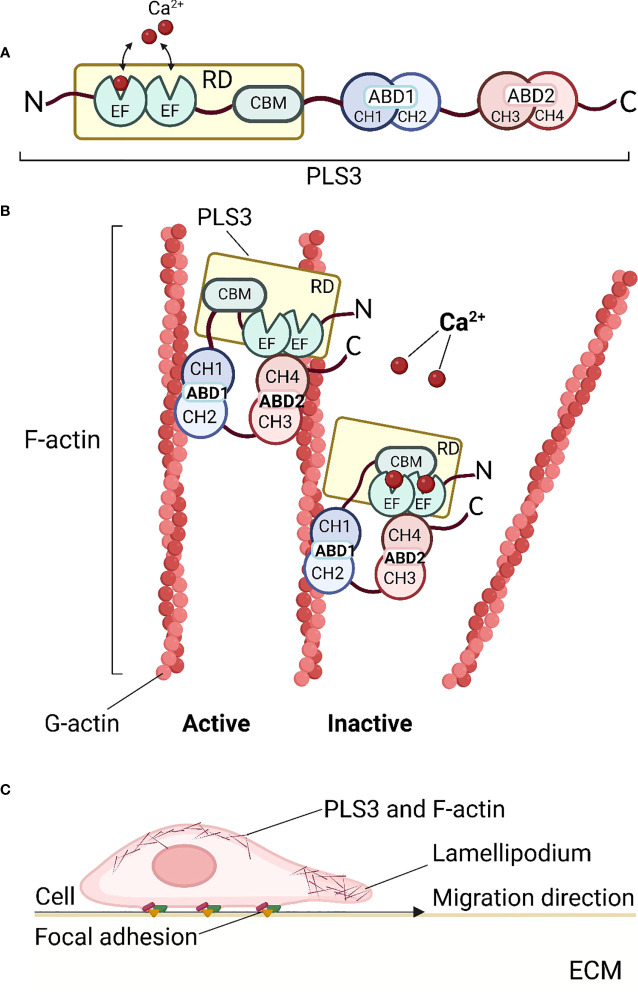
Figure 1.
Structure and function of PLS3. (A) Schematic diagram of the PLS3 protein domain structure. The N-terminus of PLS3 is linked with the Ca2+-binding regulatory domain (RD), consisting of two EF-hand motifs and the calmodulin-binding motif (CBM). RD is followed by two actin-binding domains (ABD) - ABD1 and ABD2, both of which include two tandem calponin-homology (t-CH) domains, CH1, 2 and CH3,4 respectively. (B) Actin cytoskeleton remodeling by binding and bundling of PLS3. In the active state, when Ca2+ ions are absent, PLS3 binds two filamentous actin (F-actin) molecules, consisting of globular actin (G-actin) subunits. In the presence of Ca2+ ions PLS3 is inactive and the actin filament is released. (C) PLS3 and cell motility. As a component of the cytoskeleton involved in F-actin dynamics, PLS3 participates in cell migration through the extracellular matrix (ECM), focal adhesions, and actin cytoskeleton shaping near cell membranes. ABD1, 2, actin-binding domain 1, 2; CH1, 2, 3, 4, calponin-homology domain 1, 2, 3, 4; CMB, calmodulin-binding motif; ECM, extracellular matrix; EF, EF-hands domain; F-actin, filamentous actin; G-actin, globular actin; RD, regulatory domain. Figures were created with BioRender.com.