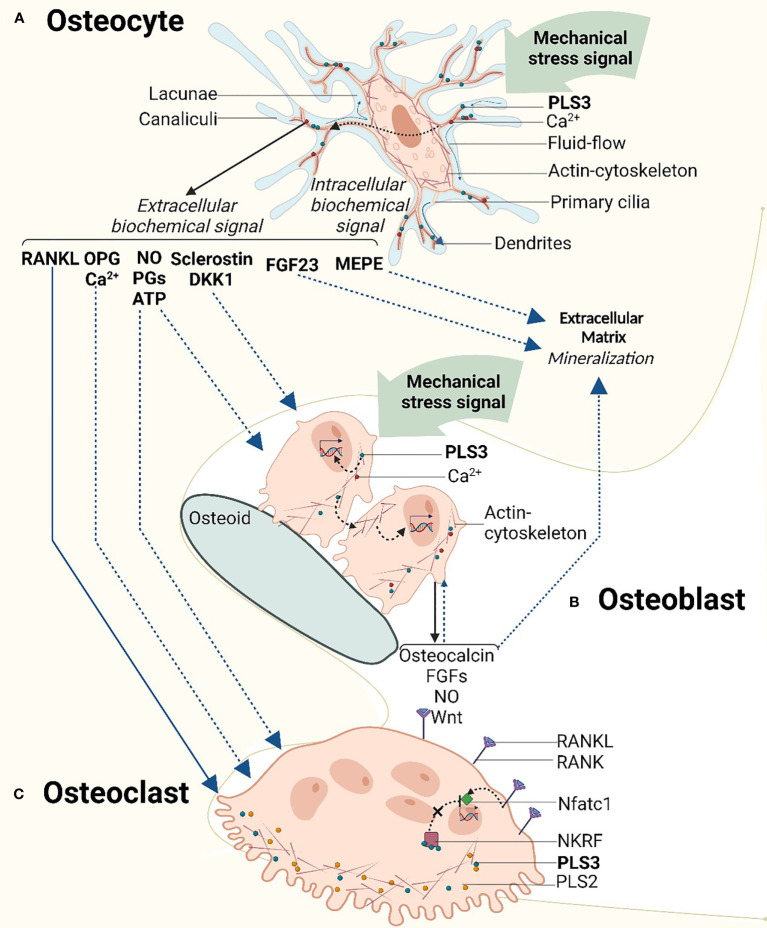
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the mechanosensory signaling cascade in relation to the cellular function of PLS3 in bone cells. (A) Mechanosensory function of PLS3 and calcium ion (Ca2+) oscillation in osteocytes. As a component of the mechanosensing actin cytoskeleton which is located in osteocyte dendrites, PLS3 reacts to mechanical stimuli activating a cascade of intracellular biochemical signals. Mechanical loading-induced Ca2+ oscillation triggers downstream signaling molecules of extracellular signaling pathways of bone metabolism. (B) Mechanical loading and PLS3 effects on osteoblasts and extracellular matrix mineralization. Mechanical stress in osteoblasts activates the production of signal molecules and growth factors similar to osteocytes, inducing the mineralization of the extracellular matrix. (C) TPLS3 in osteoclasts. PLS3 regulates osteoclast activity via the NFκB signaling pathway. DKK1, Dickkopf WNT Signaling Pathway Inhibitor 1; FGFs, fibroblast growth factors; FGF23 - fibroblast growth factor 23; MEPE, matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein; Nftac1, nuclear factor activated T cells c1; NKRF, NFκB-repressing factor; NO, nitric oxide; OPG, osteoprotegerin; PGs, prostaglandins; PLS3, t-plastin; RANK, receptor activator of nuclear factor κB; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand. Solid lines indicate pathways with solid evidence. Dashed lines indicate pathways with emerging evidence. Figures were created with BioRender.com.