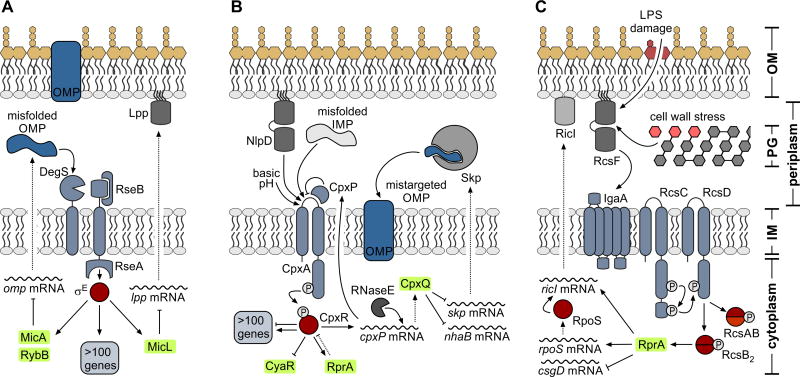
FIGURE 2.
The role of sRNAs in the major envelope stress responses. Gram-negative bacteria are diderm, with the outer membrane (OM) and inner membrane (IM) being separated by the periplasmic space containing the peptidoglycan (PG) cell wall. (A) OM homeostasis is regulated by the RpoE (σE) response. A series of proteolysis steps results in the degradation of the anti-sigma factor RseA and concomitant release of RpoE. The large regulon of the alternative sigma factor also comprises at least three sRNAs: MicA and RybB function to down-regulate the transcripts of all major OMPs to reduce the accumulation of misfolded porins within the periplasm. MicL specifically represses translation of the lpp mRNA. (B) Maintenance of the IM relies on the CpxA-CpxR TCS which amongst other targets controls expression of at least three sRNAs, CyaR, RprA and CpxQ. CpxQ is a stable fragment released by RNaseE processing from the 3’ end of the cpxP mRNA. In association with Hfq, CpxQ functions to repress translation of several transcripts including skp mRNA which encodes for a periplasmic chaperone promoting the mistargeting of OMPs into the inner membrane. (C) The IM-associated histidine kinase RcsC, phosphotransfer protein RcsD and the response regulator RcsB constitute the core of the Rcs system. The sRNA RprA is one highly induced component of the Rcs responsem which is activated by LPS damage and perturbations of the cell wall. While acting as a negative regulator of the csgD mRNA, RprA also promotes translation of both the rpoS and the ricI messages. As transcription of ricI (encoding for an inhibitor of the conjugation machinery) is dependent on RpoS, RprA functions at the heart of a post-transcriptional feed-forward loop for RicI activity.