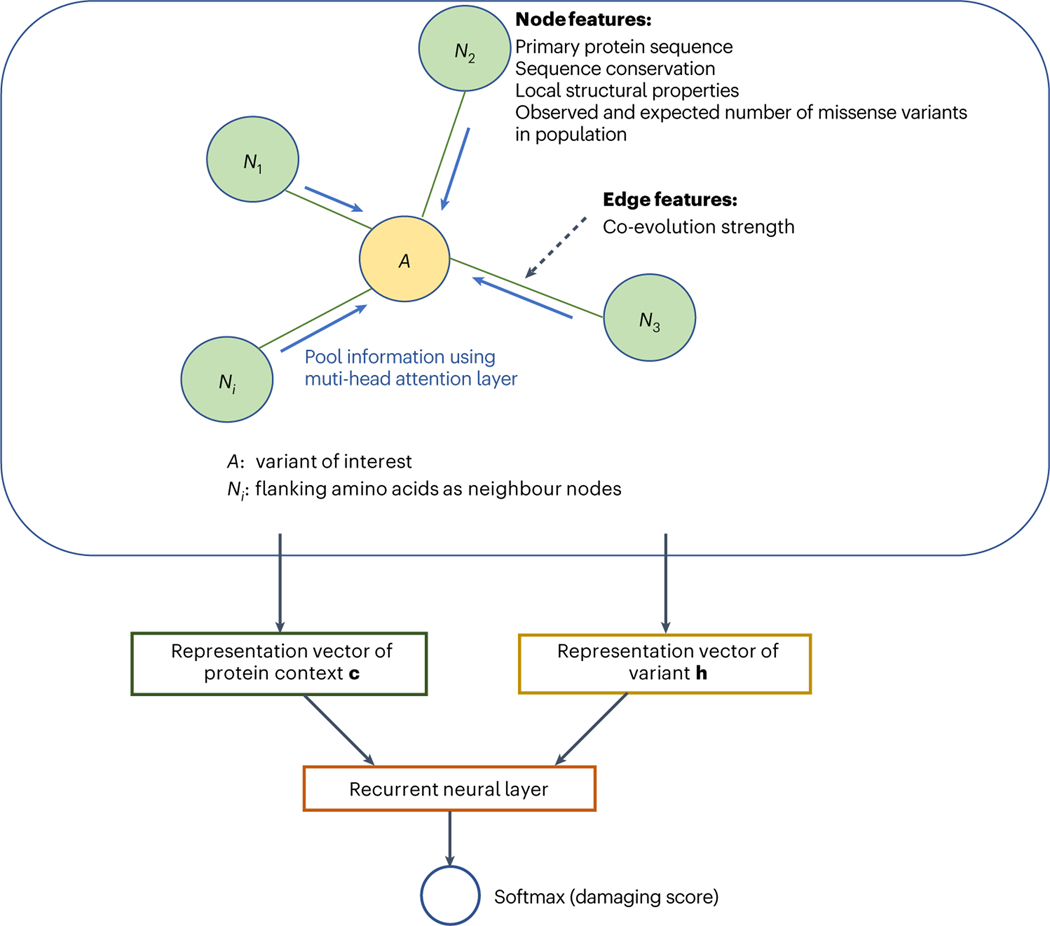
Fig. 1 |. An overview of gMVP model.
gMVP uses a graph to represent a variant and its protein context defined as 128 amino acids flanking the reference amino acid. The amino acid of interest is the centre node (coloured orange) and the flanking amino acids are the context nodes (coloured light green). All context nodes are connected with the centre node but not each other. The edge feature is co-evolution strength. The node features include conservation and predicted structural properties. Centre node features also include the amino acid substitution; context node features include the primary sequence and the expected and observed number of rare missense variants in human population. We use three one-depth dense layers to encode the input features to latent representation vectors and used a multi-head attention layer to learn context vector c. We then use a recurrent neural layer connected with softmax layer to generate prediction score from c and the representation vector h of variant.