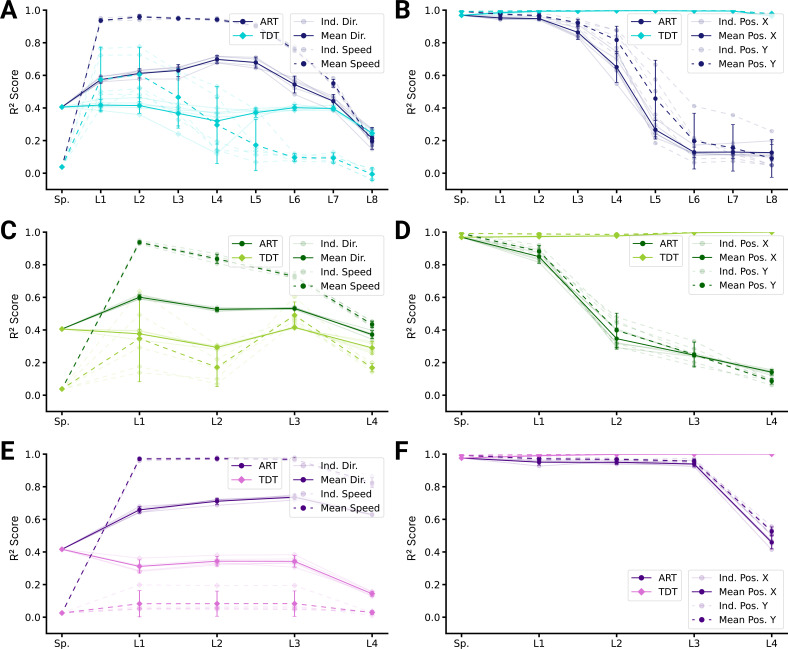
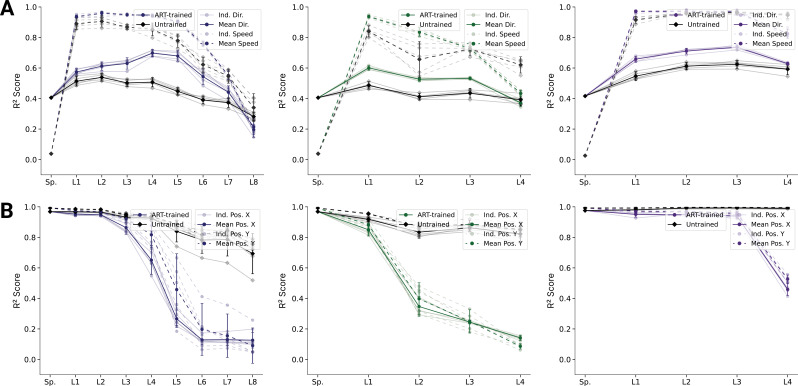
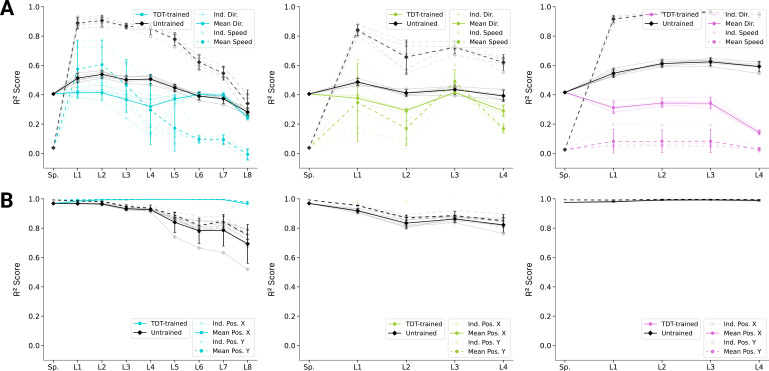
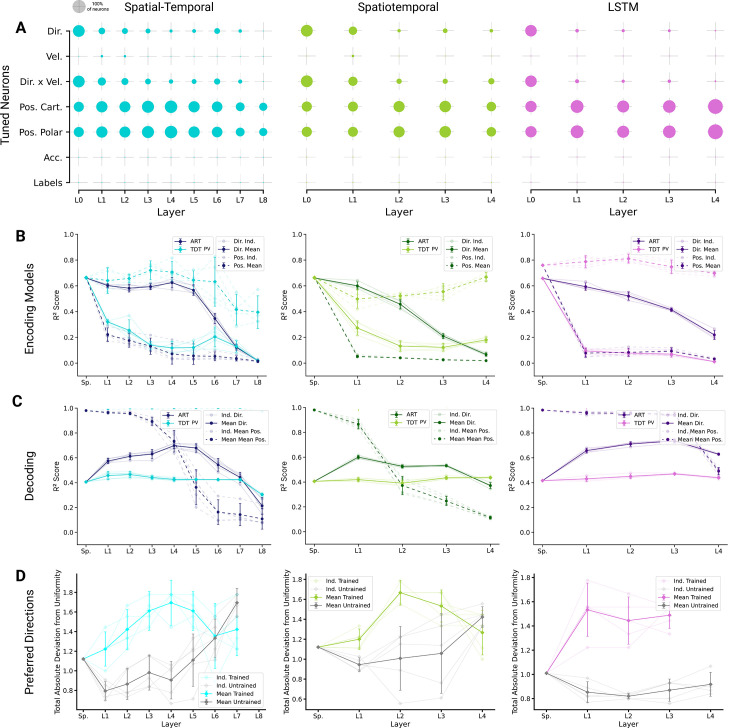
(A) For an example instantiation, the fraction of neurons that are tuned for a particular feature ( on the relevant encoding model). Model architectures: (left) spatial-temporal, (middle) spatiotemporal, (right) long short-term memory (LSTM). Tested features were direction tuning, speed tuning, velocity tuning, Cartesian and polar position tuning, acceleration tuning, and label tuning (328/5446 scores excluded for TDT-PV-trained spatial-temporal model, 140/3262 for spatiotemporal, and 1150/9142 for LSTM; see Methods). (B) The means of 90% quantiles over all five model instantiations of models trained on action recognition task (ART) and TDT-PV are shown for direction tuning (dark) and position tuning (light). 95% confidence intervals are shown over instantiations (). (C) Population decoding of direction (dashed) and Cartesian coordinates (solid; mean over individually computed scores for X and Y directions taken) for the ART-trained and TDT-PV-trained for spatial-temporal models (left), spatiotemporal (middle), and LSTM (right) models. The faint line shows the score for an individual model; the dark one the mean over all instantiations (). (D) For quantifying uniformity, we calculated the total absolute deviation from the corresponding uniform distribution over the bins in the histogram (red line in inset) for the spatial-temporal model (left), the spatiotemporal model (middle), and the LSTM model (right). Normalized absolute deviation from uniform distribution for preferred directions per instantiation is shown (, faint lines) for TDT-PV-trained and untrained models as well as mean and 95% confidence intervals over instantiations (solid line; ).