Figure 3. Major glycerophospholipids – synthesis and potential signaling applications.
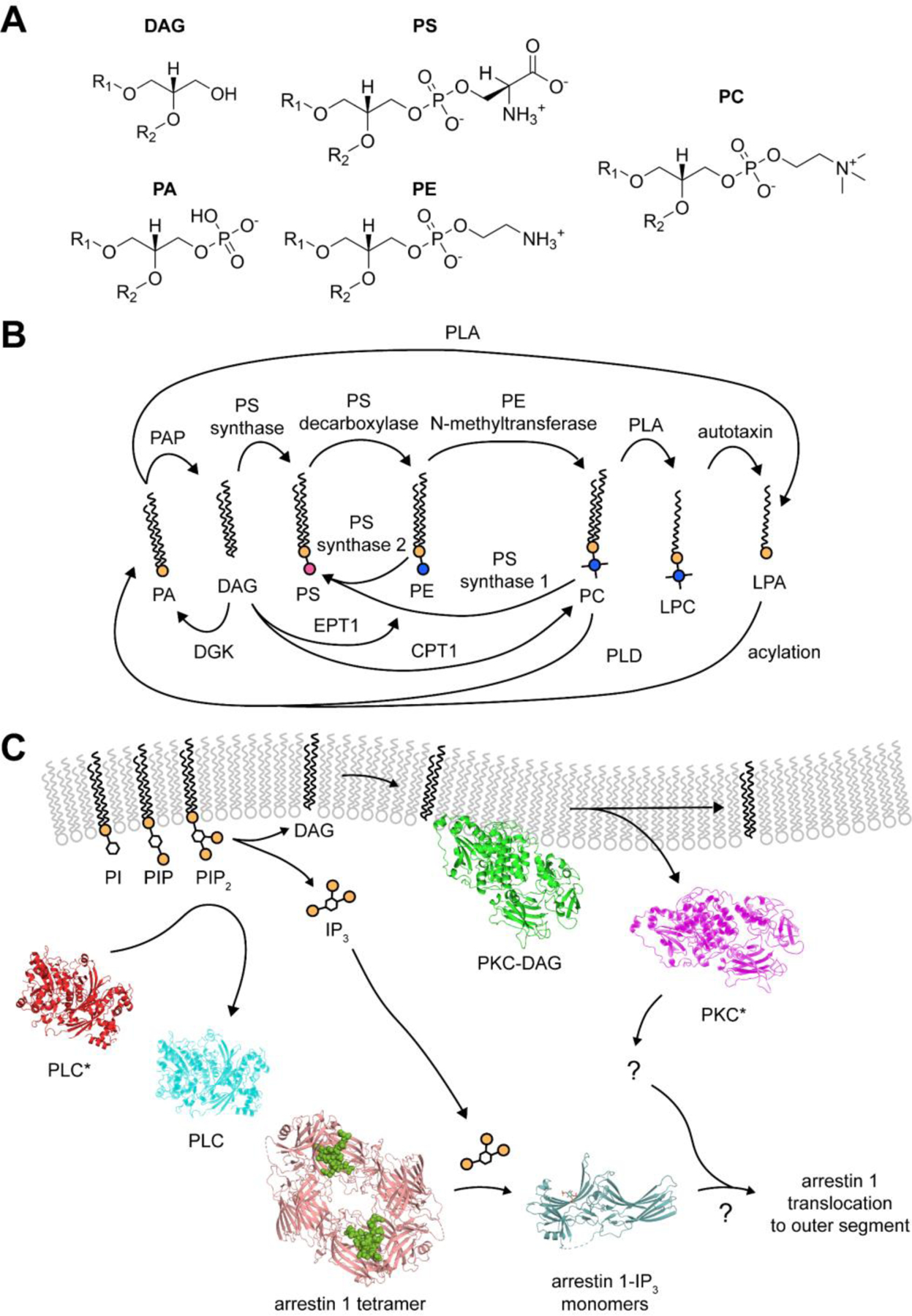
(A) Chemical structure of the five major glycerolipids. (B) Major glycerophospholipid pathways. Many enzymes are involved in the interconversion of each lipid species, including (C) Proposed involvement of IP3 and DAG in arrestin 1 translocation. Structures from a recent study of arrestin 1 in complex with IPs showed their ability to displace the arrestin 1 C-terminus, which is essential for inner-segment localization. The combination of a new basal structure, IP-complex structures, and data from Orisme et al. suggest a possible molecular mechanism for arrestin 1 translocation in cases of PLC activity. PLC structures were made from PDB structure 2ZKM (Hicks et al., 2008). PKC structures made from model predicted using AlphaFold, Uniprot identifier P17252 (Jumper et al., 2021). Basal and IP3-bound arrestin-1 structures taken from PDB structures 7JSM and 7JXA (Sander et al., accepted for puvlication).
