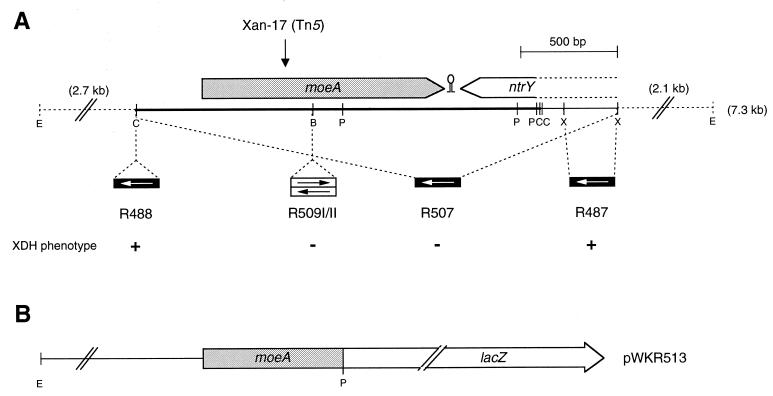
FIG. 1.
Physical and genetic maps of the R. capsulatus moeA gene region. (A) The localizations of ORFs are given by arrows carrying their respective gene designations. The vertical arrow indicates the location of the Tn5 insertion in R. capsulatus mutant strain Xan-17. The 2,005-bp ClaI fragment sequenced in this study is marked by a heavy line, and a stem-loop structure located between moeA and ntrY is indicated. Below the map, the locations of interposon insertions are shown. The direction of transcription of interposon resistance genes are symbolized by arrows in boxes (gentamicin resistance gene, white arrow; kanamycin resistance gene, black arrow), indicating polar and nonpolar insertions. The ability of the corresponding R. capsulatus mutant strains to grow with xanthine as the sole nitrogen source is indicated by a plus or minus. (B) Construction of a translational moeA-lacZ fusion. In plasmid pWKR513, an EcoRI-PstI fragment was fused to the reporter gene lacZ located on the broad-host-range vector plasmid pPHU235. Abbreviations: B, BamHI; C, ClaI; E, EcoRI; P, PstI; X, XhoI.