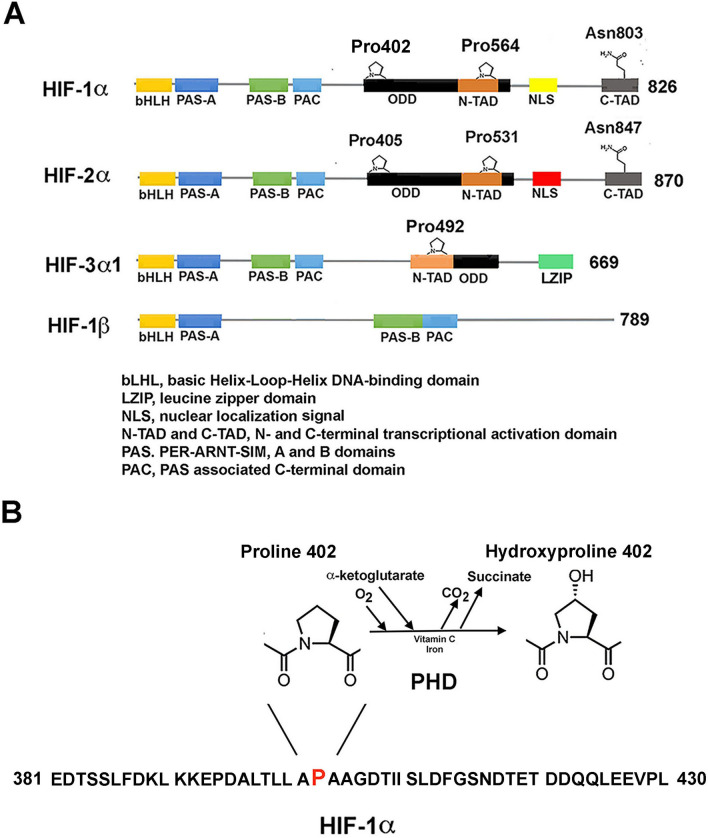
Fig. 2.
Protein domain arrangement of HIF proteins. A Schematic representation of the structural domain organization of HIF proteins belonging to bHLH/PAS protein family of transcriptional regulators: three HIF-α paralogs (HIF-1α, HIF-2α and HIF-3α) and the common interacting partner, HIF-1β (ARNT). Starting from the N-terminus, the following domains are present: bHLH, basic helix–loop–helix DNA-binding domain; PAS, PER-ARNT-SIM, A and B tandem domains, required for protein–protein binding and dimerization; PAC, PAS-associated C-terminal domain. HIF-α paralogs also present an ODD, oxygen-dependent degradation domain; N- and C-term TAD, transactivation domains, involved in the transcriptional activation. Other highlighted motifs are: NLS, nuclear localization sequence; L-ZIP, leucine zipper, DNA-interacting motif present at the C-term of HIF-3α. Specific hydroxylated (Pro402, Pro564, and Asn803 in HIF-1α and Pro405, Pro531, and Asn847 in HIF-2α) and ubiquitinated residues (Ub, Lys 467 in HIF-1α) and the enzymes responsible for the post-translational modification are reported. PHD(1–3), Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain-containing enzyme; VHL, Von Hippel-Lindau protein. B Schematic representation of the reaction of hydroxylation on Pro402 of HIF1α by PHD