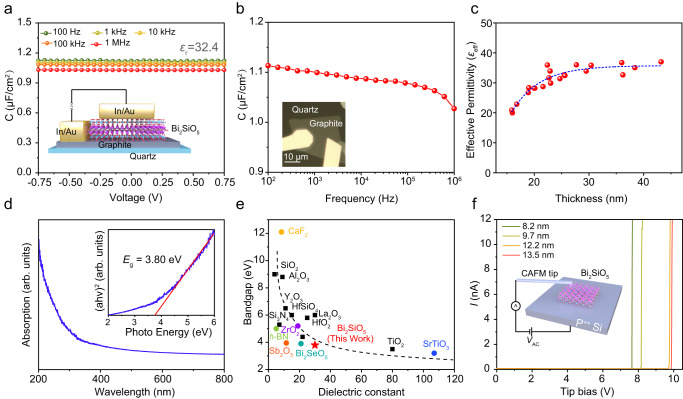
Fig. 2. Dielectric constant, band gap, and breakdown field strength of CVD-grown Bi2SiO5 nanoflakes.
a Typical Bias-dependent capacitance (C) measurements on CVD-grown Bi2SiO5 nanoflake with a common metal-insulator-metal (MIM) device configuration, where the thick graphite and In/Au metals serve as the bottom and top electrodes (inset), respectively. The dielectric constant (ɛr) of Bi2SiO5 was estimated as ~32.4 at 100 Hz. b Corresponding frequency-dependent capacitance (C–f) characteristics of the MIM device, whose OM image is inset in b. c The thickness-dependent effective permittivity (εeff) of Bi2SiO5 nanoflakes with a measuring frequency of 100 Hz. The dashed blue curve is a visual guide. d Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) absorption spectrum of CVD-grown Bi2SiO5 nanoflakes transferred onto quartz substrate with high coverage by mechanical pressing. The inset shows the fitting of its optical band gap (~3.8 eV) by Tauc’s law, where a, h, and ν are the absorption coefficient, Planck constant and frequency, respectively. e Energy band gap versus dielectric constant of representative dielectric materials in literature, showing the coexistence of high dielectric constant and large band gap in Bi2SiO5. The dashed line is a visual guide. f Thickness-dependent current-voltage curves of Bi2SiO5 nanoplates measured by C-AFM, showing a high breakdown field strength of 9.4 MV/cm (8.2 nm).