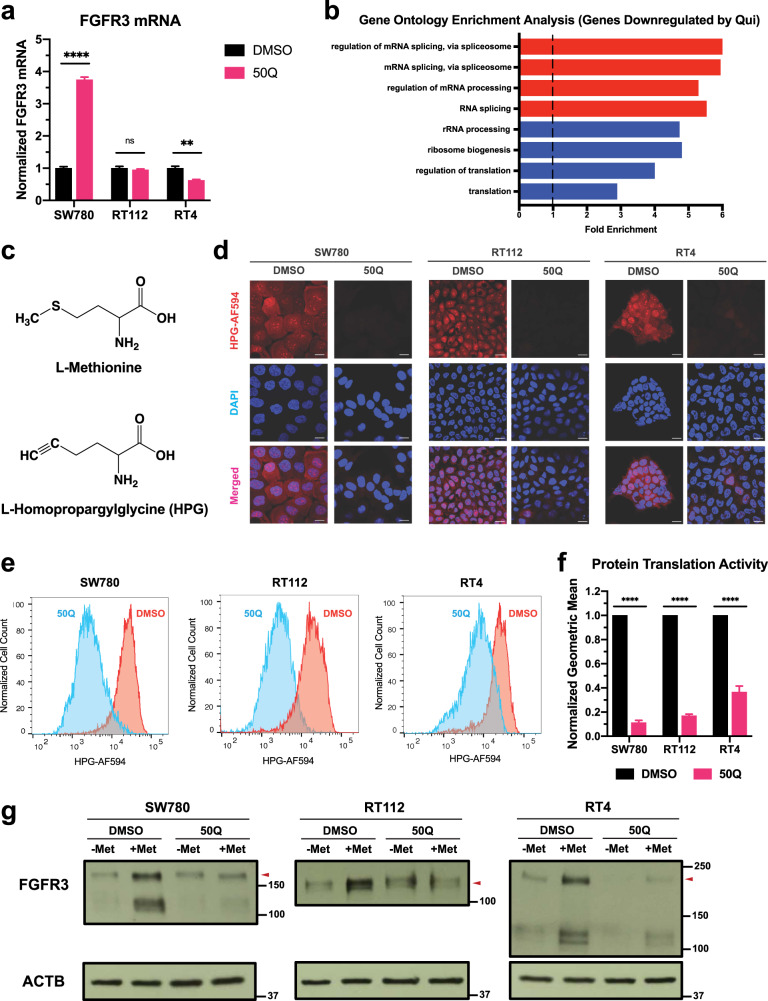
Fig. 5. Quisinostat downregulates FGFR3 fusions by suppressing FGFR3 translation.
a RT-qPCR results showing the FGFR3 mRNA level with or without quisinostat treatment in all three BC cells. All results were first normalized to β-actin (ACTB) loading control and then normalized to DMSO control of each cell line. Data were plotted as mean ± SEM from four biological replicates and statistics were calculated by t tests (ns, non-significant; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001). b Gene ontology enrichment analysis of the RNA-seq results reveals that genes involved in protein translation are more likely to be downregulated by quisinostat in all three BC cells (log2Fold-change < −0.3). c Chemical structures of L-methionine and L-homopropargylglycine (HPG). d Microscopic results of total protein translation assays with or without the treatment of quisinostat. Cells were first treated by quisisnostat for 2 days and then analyzed by total protein translational assays. Scale bar: 16 µm. e Flow cytometry results of total protein translation assays with or without the treatment of quisinostat. Cells were first treated by quisisnostat for 2 days and then analyzed by total protein translational assays. Cell counts were normalized to the mode of each sample. f Normalized geometric means of (e). Quisinostat treatment can decrease total protein translation to ~10–40%, depending on the cell line. Geometric means of each sample were normalized to the DMSO control of each cell line. Data were plotted as mean ± standard deviation from three biological replicates and statistics were calculated by t tests (****p < 0.0001). g Western blots showing FGFR3 translation with or without quisinostat treatment in all three BC cells. Cells were first treated by quisinostat or DMSO for 2 days and then starved by no L-methionine media overnight. L-methionine was then added into the culture media and cells were incubated for another 8 h. After that, cells were harvested for western blotting. β-actin (ACTB) was used as standard loading control. 50Q, 50 nM quisinostat; Met, L-methionine.