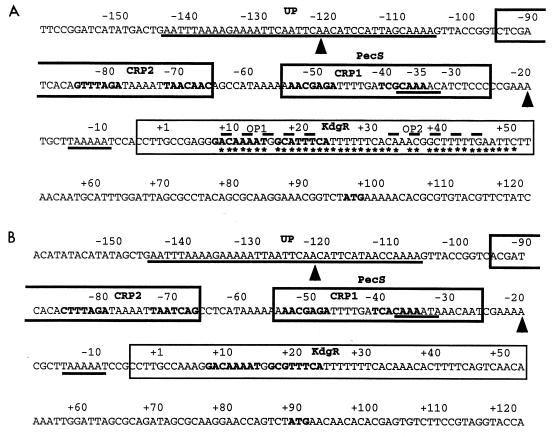
FIG. 2.
Organization of the promoter-operator region of the E. chrysanthemi EC16 pelE (A) and 3937 pelD (B) genes. The sequences are numbered from the transcription start site (+1, G base). The regions protected by the various regulatory proteins are delineated based on the examination of both DNA strands. Regions corresponding to the −10/−35 promoter sites and the AT-rich region protected by RNAP, and which include the sequence showing homology with the consensus (AAA[A/T][A/T]T[A/T]TTTT--AAAA) proposed by Ross et al. (26) (putative UP elements), are underlined; arrowheads indicate the ends of the region protected by PecS in DNase I footprinting experiments; the sequences boxed with bold and solid lines indicate the binding sites for cAMP-CRP and KdgR, as defined by DNase I footprinting experiments, respectively; the nucleotides in bold, located in the boxed regions, correspond to the sequences that show homology with the consensus binding site for cAMP-CRP (AATGTGAN6TCACATT [15]) and KdgR ([AATAGAAATC]N[NCATGTTTTCA] [19]), respectively; the regions corresponding to the previously proposed OP1 and OP2 by Gold et al. (12) are overlined by dashed lines; the ATG translation initiation codons are indicated in bold; on the EC16 pelE operator, asterisks indicate the nucleotides contacting the KdgR repressor, as deduced from base removal experiments.