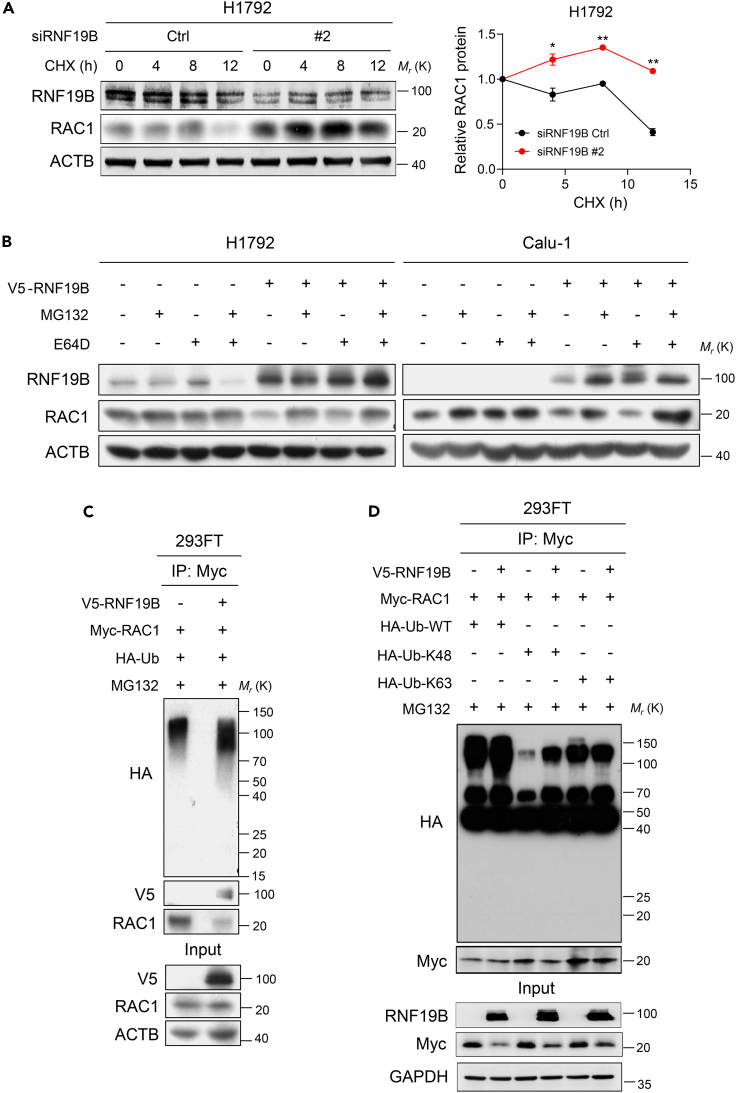
Figure 5.
RNF19B catalyzes K48-linked polyubiquitination of RAC1
(A) Left: Knockdown of RNF19B expression by RNF19B-2 siRNA in H1792 cells in the presence or absence of cycloheximide (CHX) at 10 μg/mL for the indicated times (0, 4, 8, and 12 h). Cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against RNF19B, RAC1, and ACTB. Right: The band intensity of RAC1 was quantified by ImageJ software and plotted. This experiment was repeated three times independently with similar results (mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; p-values were obtained using two-tailed Student’s t-tests).
(B) H1792 and Calu-1 cells were transfected with V5-RNF19B or control plasmid and were cultured for 24 h before being further incubated with MG132 (20 μM) or E64D (15 μM) for 6 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against RNF19B, RAC1, and ACTB.
(C) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of the ubiquitination of RAC1 in 293FT cells co-transfected with V5-RNF19B plasmid, Myc-RAC1 plasmid, and HA-Ub plasmid.
(D) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of the ubiquitination of RAC1 in 293FT cells co-transfected with V5-RNF19B plasmid, Myc-RAC1 plasmid, and HA-Ub-WT, HA-Ub-K48, or HA-Ub-K63 plasmid.