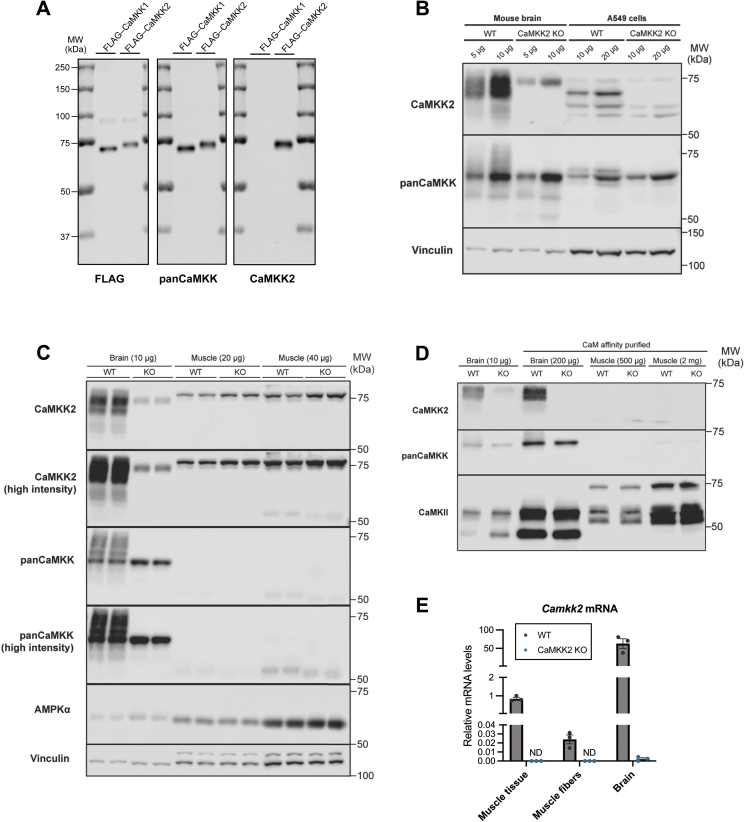
Figure 5.
CaMKK2proteinis undetectable in mouse skeletal muscle. (A) Validation of isoform-specificity of CaMKK antibodies. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged CaMKK1 or CaMKK2. Affinity purification was performed using FLAG-agarose beads and the equal amount of purified FLAG-CaMKK1 or FLAG-CaMKK2 were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. (B) Immunoblot analysis of CaMKK isoforms in wild-type (WT) and CaMKK2 knock-out (KO) mouse brain and A549 cell lysates. (C) Different amounts of skeletal muscle (gastrocnemius) or brain lysates from WT and CaMKK2 KO mice were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. Immunoblots with pan-CaMKK and CaMKK2 antibodies were visualized at either lower or higher intensity. (D) Calmodulin (CaM) affinity purification was used to enrich for CaM-binding proteins which were subsequently subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. Representative blots from three independent experiments are shown. Mouse samples used in panels (B–D) are from male, 17–18-week-old mice. (E) Levels of Camkk2 mRNA expression in WT or CaMKK2 KO skeletal muscle (gastrocnemius) tissue, isolated skeletal muscle (gastrocnemius) fibers and brain were determined by qPCR using Taqman probes (n = 3). Shown values are relative to WT skeletal muscle tissue. ND represents non-detected levels.