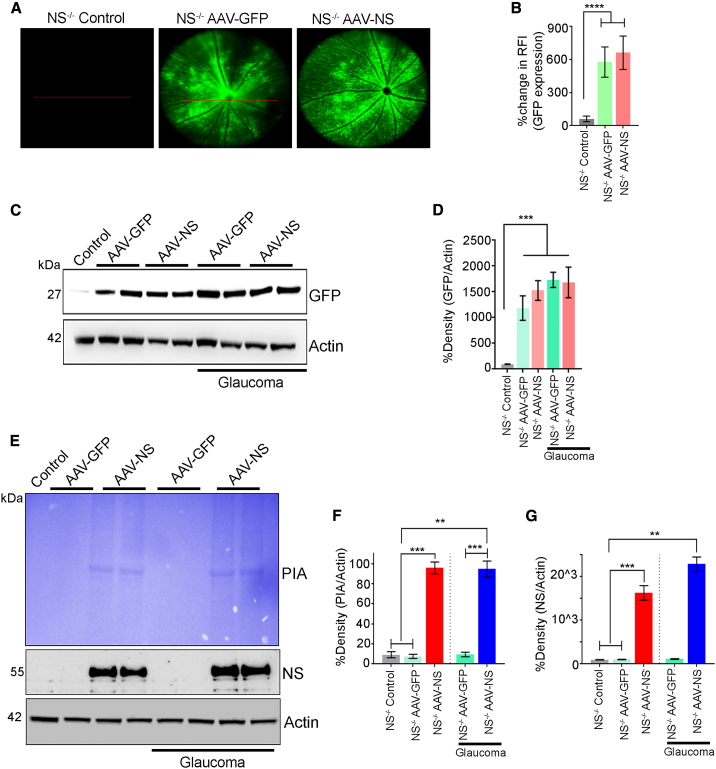
Figure 6.
NS expression and plasmin inhibitory activity (PIA) in NS-ablated mice under control and glaucoma conditions
(A) Fundus photographs showing GFP expression 2 months after intravitreal administration of AAV2 vectors in mouse retinas. (B) Quantification of the relative fluorescence intensity (p < 0.0001, n = 10 animals/group). (C) WB analysis of ONH lysates revealed expression of GFP in AAV-treated NS−/− mouse retinas. (D) GFP fold changes relative to control NS−/− mice retina under control and glaucoma conditions. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 10 animals/group, p < 0.005, ANOVA). (E) ONH lysates from control and AAV-GFP- and AAV-NS-treated NS−/− retinas under normal and high-IOP conditions were subjected to gelatin zymography to evaluate the PIA of NS. The blots were also probed for NS immunoreactivity in each case (n = 3 each). (F) Relative band intensities were quantified, and data analysis indicated that overexpression of NS in NS-ablated mice has significantly higher PIA under normal and glaucoma conditions (p < 0.003 and p < 0.005; n = 3 animals/group). (G) Significantly higher NS expression compared with control and AAV-GFP treatment under both control (p < 0.006) and glaucoma conditions was observed (p < 0.003, n = 3 animals/group).