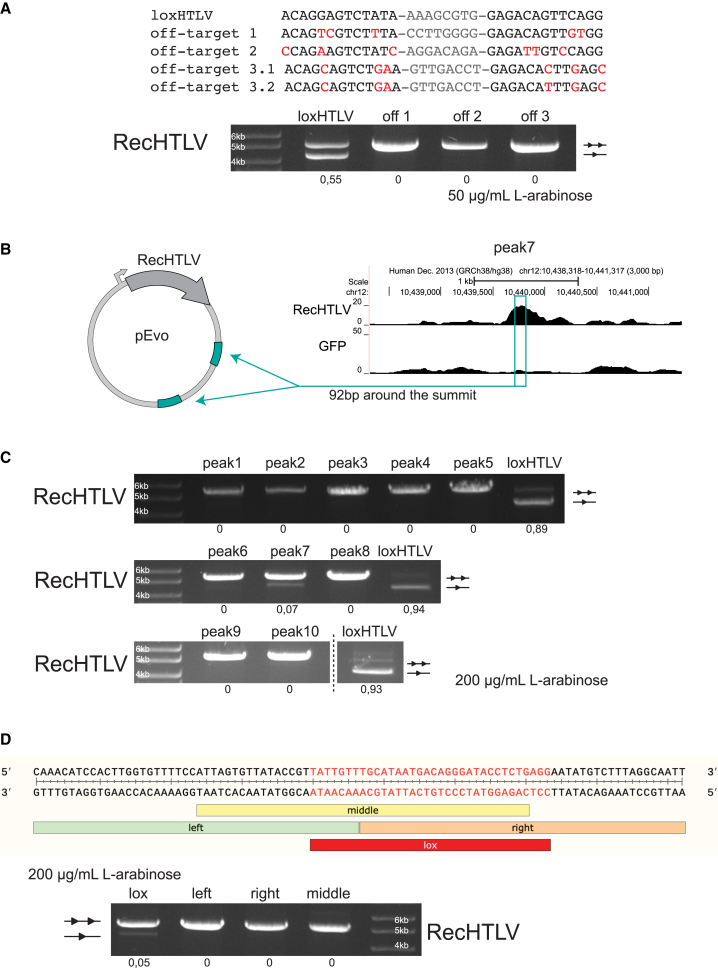
Figure 5.
Off-target analysis of RecHTLV
(A) Top: alignment of the loxHTLV target sequence to the in-silico-predicted off-target sites: 1, 2, and 3. Off-target site 3 is asymmetric and is therefore shown as 3.1 and 3.2 in the alignment. Mismatches to the loxHTLV sequence are marked in red and spacers are shown in gray. Bottom: agarose gel showing the recombination activity of RecHTLV at 50 μg/mL L-arabinose for the on-target sequence (loxHTLV) and the three predicted off-targets in bacteria. Off-target sites 1 and 2 were inserted twice as excision substrates in the pEVO vector, whereas off-target site 3 consists of the 3.1 and the 3.2 sequences inserted as excision substrates. Below each lane, quantification of the recombination efficiency is shown. The upper unrecombined band is indicated with two triangles and the recombined band with one triangle. (B) Schematic representation of the plasmids used for testing the selected peaks from the ChIP-seq experiment in bacteria. From the selected peaks, 92 bp around the summit of the peak were cloned twice in the pEVO vector as excision substrates. (C) Bacterial plasmid-based for RecHTLV activity assay of the 10 peaks selected from the ChIP-seq binding sites. All peaks were tested at 200 μg/mL of L-arabinose. Quantification of the recombination is shown below each lane. (D) Dissecting peak 7 to find the RecHTLV recombinase recognition sequence. Top: sequence of the 92 bp tested in the plasmid assay with the indicated subdivisions tested: “left”, “middle”, “right” “lox”. Bottom: agarose gel from the bacterial test digest assay showing the recombination efficiencies of the different parts of peak 7. Only the lox-peak7 sequence shows recombination at 200 μg/mL L-arabinose. Quantification of the recombination is shown below each lane. The upper unrecombined band is indicated with two triangles and the recombined band with one triangle.