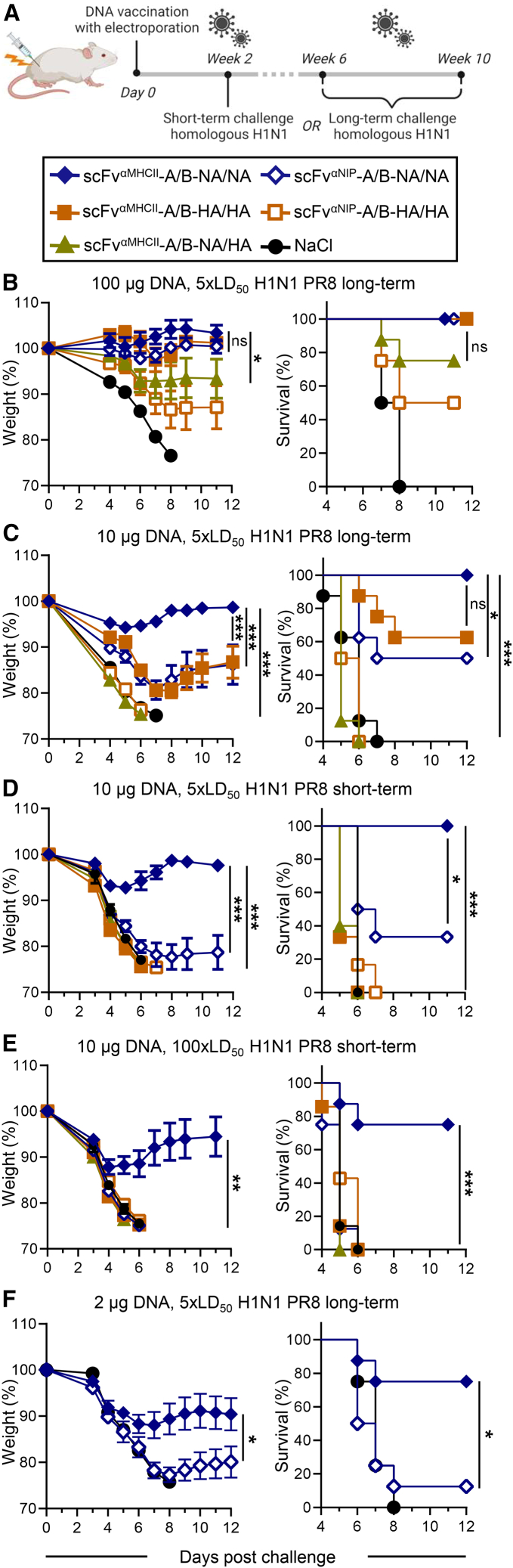
Figure 4.
A single DNA immunization with MHC class II-targeted NA/NA vaccines protects against homologous influenza virus challenge
(A) BALB/c mice were immunized once i.m./EP and challenged with homologous influenza A H1N1 PR8 virus at week 2 (short term) or between weeks 6 and 10 (long term) after vaccination. (B–F) 50 μg of each A and B plasmids (total 100 μg, B), 5 μg/plasmid (10 μg total, C–E), or 1 μg/plasmid (2 μg total, F) of the indicated DNA vaccines (box) were used. Mice were challenged with a lethal dose of 5× LD50 (B–D and F) or 100× LD50 (E) at week 9 (B), week 10 (C), week 2 (D and E), or week 6 (F). Weight (left, mean ± SEM) and survival (right) were monitored up to 12 days post challenge. n = 8 mice/group (B, C, E, and F) or n = 6 mice/group (D). Dead mice were assigned a weight of 75%. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001; two-way ANOVA (weight curve) or Mantel-Cox test (survival). Statistical analysis compared MHC class II-targeted NA/NA versus HA/HA as well as targeted versus non-targeted and antigen-bivalent versus -monovalent NA.