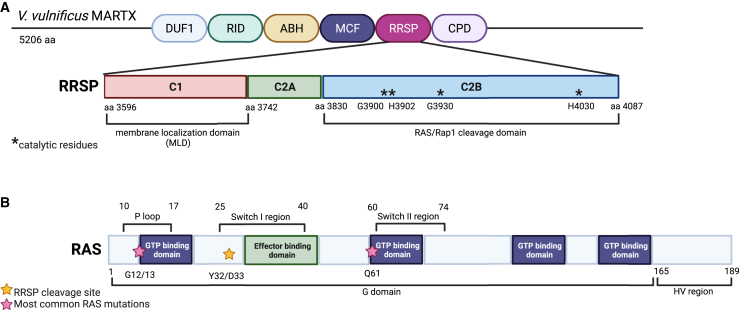
Figure 3.
Functional domains within RRSP and RAS
(A) Schematic of RRSP from the Vibrio vulnificus MARTX toxin. The V. vulnificus MARTX is composed of six effector domains, including RRSP. The RRSP effector has three functional domains: C1, C2A, and C2B. C1 is the membrane localization domain and C2B contains the catalytic domain of RRSP. The function of the C2A domain is unknown. Within the C2B domain, four residues (denoted with asterisks) are critical for RAS/Rap1 cleavage. These include G3900, H3902, G3930, and H4030. If these residues are mutated catalytic activity is significantly reduced.115,117,132 (B) Schematic of the key functional domains of the RAS proteins. The RAS proteins (HRAS, NRAS, KRAS4A, and KRAS4B) have high sequence homology other than the C-terminal domain termed the hypervariable (HV) region. RAS proteins contain a P loop and Switch I/II regions.4,10 These three domains all are subject to the most common mutations found in RAS-driven cancers. The P loop and Switch II region each contain a GTP-binding domain and are the sites for the most frequent mutations G12/13 and Q61 (denoted with pink stars). The Switch I region contains the effector binding domain. RRSP cleaves RAS within this region between the residues Y32 and D33 (denoted with a yellow star), thus interfering with RAS downstream effector activation. Figure created with Biorender.com.