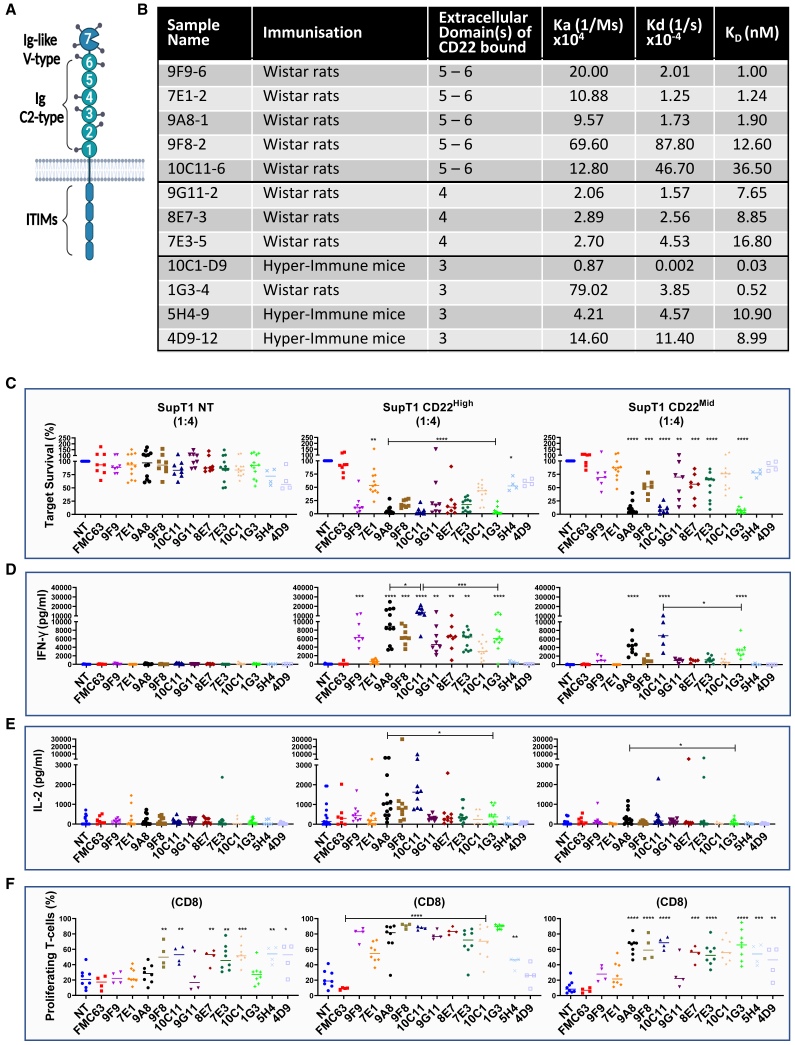
Figure 1.
Screening of novel binders recognizing CD22
(A) CD22 is a large protein bearing an ectodomain of seven Ig domains. The C2 type Ig domains are labeled 1–6, with domain 6 being the most proximal to-the-membrane domain. (B) Wistar rats or hyper-immune Abverimice were immunized against CD22 ectodomain to obtain novel binders recognizing against CD22. The biophysical properties of the binders, such as the Ig domain recognized and kinetics, are shown in (B). (C) All binders were incorporated into a retroviral cassette into a Fab CAR format and screened against the non-specific SupT1 NT cell line, or SupT1 cells engineered to express high- or mid-CD22 density. CAR T cells were challenged with 5 × 104 SupT1 NT, CD22High, or CD22Mid for 72 h at a 1:4 E:T ratio. We measured the secretion of IFN-γ (D) and IL-2 (E) by ELISA. The supernatant was harvested from a co-culture of 5 × 104 target cells with CAR T cells at 1:4, 72 h after the assay execution. (F) The proliferation of CAR T cells was validated by labeling the T cells with CTV and challenging them with 5 × 104 SupT1 NT, CD22High and CD22Mid at a 1:1 ratio. The CTV dilution was measured on day 4, and the percentage of proliferation for each CAR condition was normalized to the equivalent condition in SupT1 NT for CD8 cells. One-way ANOVA was used to measure the statistical significance of the novel CARs compared to the negative FMC63 control. Comparisons between two CARs were carried out using Student's t-test (n = 8–12).