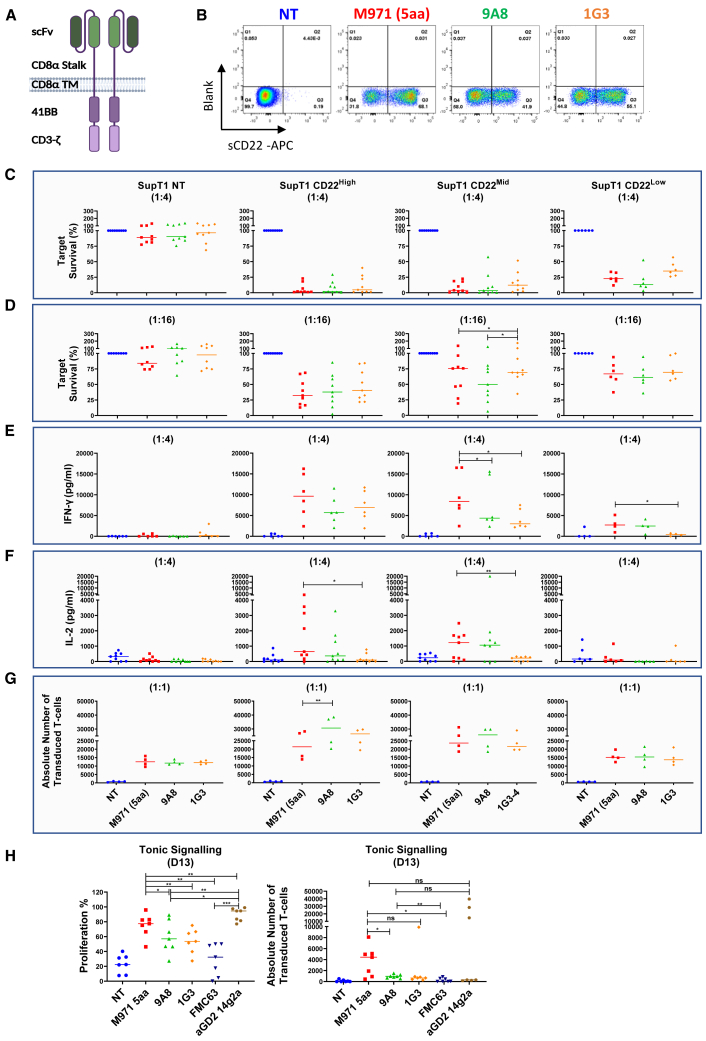
Figure 3.
Comparison of novel CD22 binding CARs to M971 in a lentiviral platform
(A) The best aCD22 CAR binders, 9A8 and 1G3, were transferred into a lentiviral EF1a promoter platform in an scFv format. (B) The expression of the transgenes on T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Specifically, T cells were labeled with biotinylated sCD22, and subsequently labeled with streptavidin-APC and Sytox Blue viability dye. A representative donor is shown in (B). The CAR cytotoxicity was measured against 1 × 105 SupT1 CD22High and CD22Mid target cells at 72 h and an E:T ratio of 1:4 (C) or 1:16 (D). An additional target was introduced, SupT1 CD22Low engineered to express approximately 490 molecules/cell. The cytokine secretion was measured by ELISA at 72 h for 1:4 E:T. The cytokines measured were IFN-γ (E) and IL-2 (F). (G) We investigated the proliferative capacity of the CARs in a 1:1 co-culture measured by the T cell expansion by day 4. (H) CAR T cells were labeled with CTV and challenged in a starvation assay without antigen stimulus or IL-2 for 13 days to measure tonic signaling. The FMC63 and aGD2 CARs were introduced as tonic signaling negative and positive controls. The statistical significance was validated by Student’s t-test. (n = 6–9).