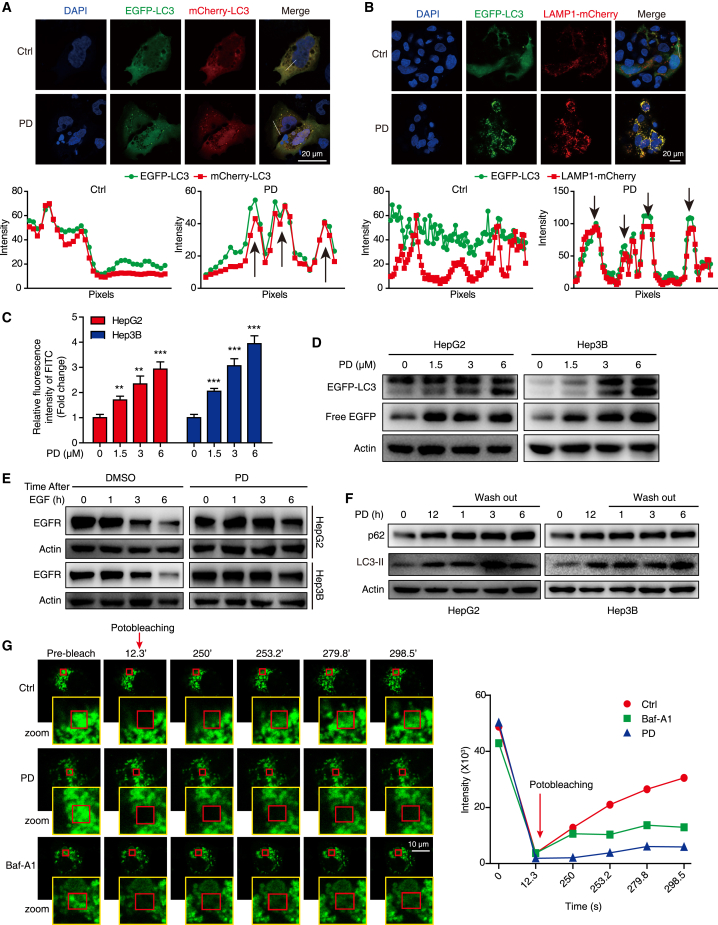
Figure 5.
PD blocks autophagic flux in HCC cells
(A) HepG2 cells transfected with mCherry-EGFP-LC3 were treated with PD (3 μM, 24 h), and photographed using confocal microscopy. The intensity profiles of EGFP and mCherry along the white line are plotted in the lower panels, with the colocalization sites marked with black arrows. (B) HepG2 cells co-transfected with the EGFP-LC3 and LAMP1-mCherry plasmids were incubated with PD (3 μM, 24 h), and then detected by confocal microscopy. The intensity profiles of EGFP-LC3 and LAMP1-mCherry along the white line were plotted in the lower panels, with the colocalization sites marked by black arrows. (C) Both HCC cell lines were loaded with FITC-dextran for 24 h and then treated with increasing concentrations of PD (0–6 μM); FITC fluorescence was detected by flow cytometry. Data are represented as the mean ± SD, n = 3; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. (D) Western blot analysis of EGFP-LC3 and free EGFP levels in EGFP-LC3 expressing HCC cells treated with increasing concentrations of PD for 24 h. (E) Cells pretreated with PD (3 μM, 12 h) were incubated with EGF (200 ng/mL, 2 h), then the medium was washed out and samples were collected at the indicated time points for IB analysis. (F) After HCC cells were treated with PD (3 μM, 12 h), then western blot analysis was performed to measure the expression of p62 and LC3-II at the indicated time points after PD washed out. (G) HepG2 cells expressing TMEM192-EGFP was incubated with DMSO (Ctrl), PD (3 μM), or Baf-A1 (200 nM, an inhibitor of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase) for 24 h, and then imaged upon photobleaching at the indicated time points. The decay of intensity was calculated in each frame, from the first frame after photobleaching to the end of the acquisition.