Figure 3. Integrated homology mapping and AlphaFold2 analysis identifies a predicted shared structure between TMEM164 and the AIG1/ADTRP lipid hydrolases.
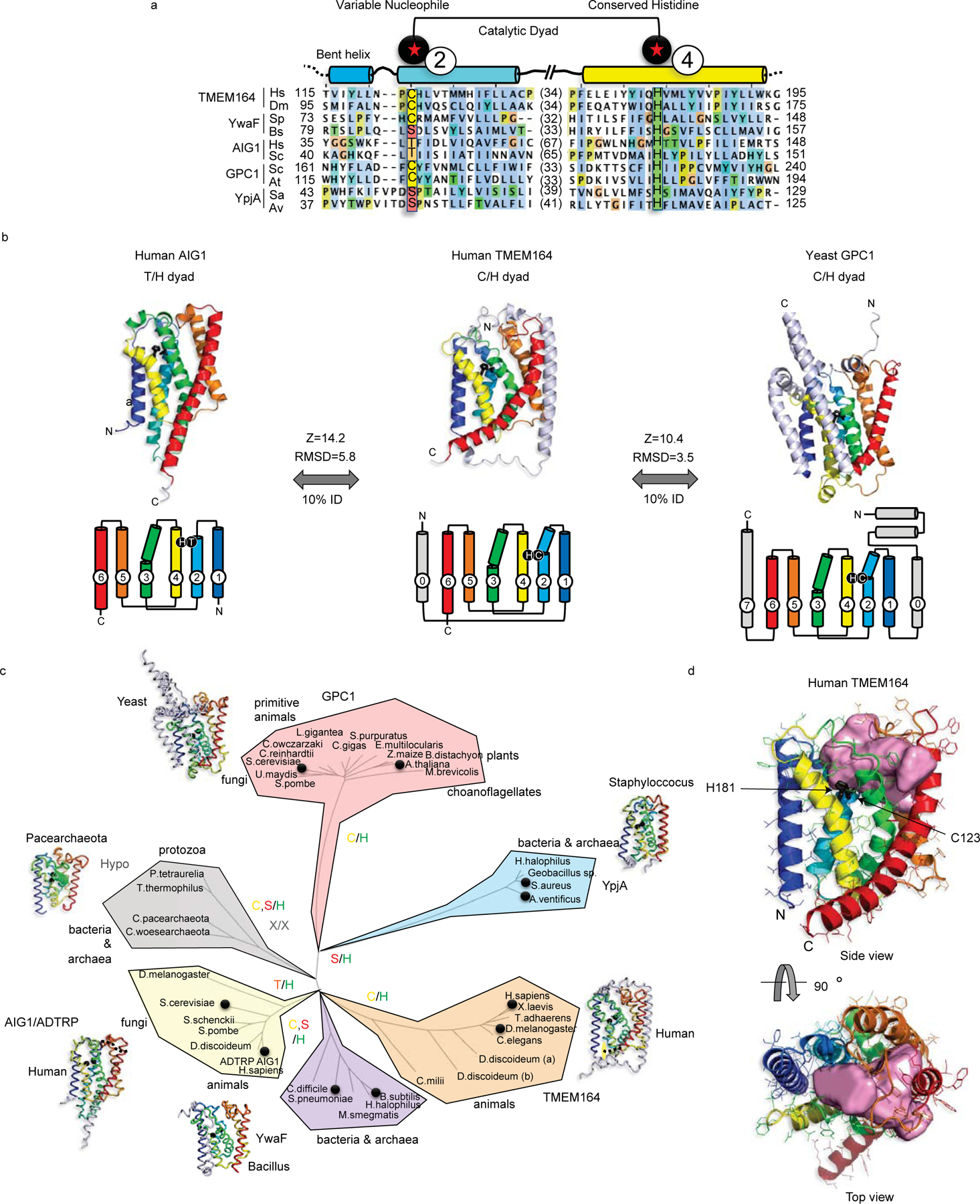
a, DALI superposition of the AlphaFold2-predicted structures of human (H.sapiens; Hs) and D. melanogaster (Dm) TMEM164 reveals a catalytic dyad of C123 and H181 in the human chain (respectively on TM helices 2 and 4 of the conserved 6TM fold) that aligns with the Thr/His dyad of AIG1-class FAHFA hydrolases (from H.sapiens and S. cerevisiae (Sc)), and defines a superfamily of nucleophile-variable/His-invariant enzymes that share a conserved membrane topology with otherwise sparse sequence identity. Prokaryotic YwaF and YpjA enzymes respectively include S.pneumoniae (Sp) and B.subtilis (Bs), and S.aureus (Sa) and A.ventificus (Av) proteins, while GPC1 enzymes are drawn from S.cerevisiae and A.thaliana (At). See Extended Data Fig. 5 for a more complete sequence alignment. b, Fold and topology comparison of human TMEM164 with human AIG1 and yeast GPC1 enzymes highlighting a 6TM core fold (with helices 1–6 color-ramped to match the topology diagrams; additional helices in grey) with active site Cys or Thr nucleophiles in blue TM2, placed opposite to the invariant His in yellow TM4 (sidechains in black stick format). Z-scores and RMSD values (in Å) for comparison of TMEM164 and AIG1 or GPC1 AlphaFold2 models are provided. c, Evolutionary tree of the AIG1/TMEM164/GPC1/YwaF/YpjA (or ATGY) superfamily drawn by DALI-derived fold similarity with variable nucleophilic residues noted in each branch. Black circles mark sequences present in the abridged alignment in a. d, CavityPlus analysis of the human TMEM164 6TM core showing an internal cavity (with predicted portals to the lipid bilayer) that abuts the C123/H181 catalytic dyad (in black stick form). Figures drawn with Jalview (http://jalview.org) and PyMOL (http://pymol.org).
