Figure 4.
Mouse hepCLiPs repopulate chronically injured mouse livers
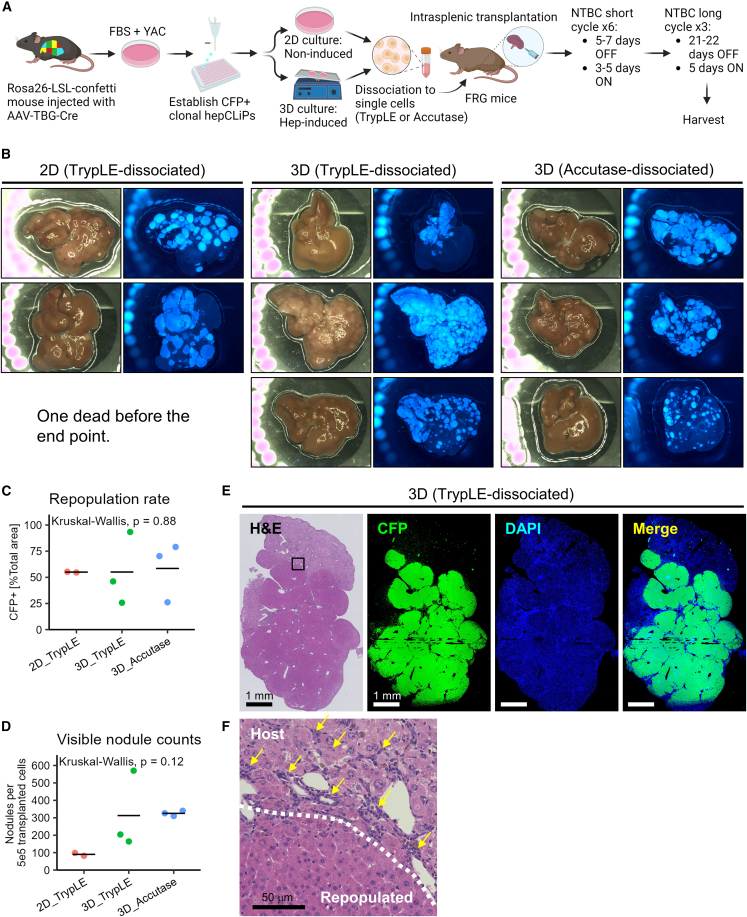
(A) Schematic of experimental design for the establishment of CFP-labeled clonal hepCLiPs and the repopulation assay for one of these CFP+ hepCLiP clones using the FRG mouse system.
(B) Macroscopic brightfield and fluorescent images of the FRG mouse livers. Livers were harvested from the host mice, which were treated with the nitisinone cycle for 3.8 months.
(C) Estimation of repopulation efficiency based on the gross fluorescent images described in (B). The horizontal bars indicate the mean values. Global p value among the three groups was calculated by the Kruskal-Wallis test.
(D) Number of nodules visible on the liver surface were counted on each image shown in (B) and represented as “per transplanted 5 × 105 cells” (note that 5 × 105 cells/mouse were transplanted for 2D_TrypLE and 3D_TrypLE groups, while 2.5 × 105 cells/mouse were transplanted for 3D_Accutase. See experimental procedures for details). The horizontal bars indicate the mean values. Global p value among the three groups was calculated by the Kruskal-Wallis test.
(E) Stitched image of an H&E-stained hepCLiP-repopulated FRG mouse liver tissue (left), and the CFP IF and DAPI counterstained images of the corresponding region are shown (right). A TrypLE-dissociated hepCLiP_3D-transplanted sample is shown as a representative image. Similar staining patterns are observed for the other two groups as shown in Figure S5. Scale bars: 1 mm.
(F) A higher magnification image of the region indicated by the rectangle in the H&E staining of Figure 4E. Scale bar: 50 μm.