Figure 5.
scRNA-seq analysis of HCOs reveals that PHOX2B-PARM interrupts the progenitor-to-neuronal transition of PHOX2B+ cells
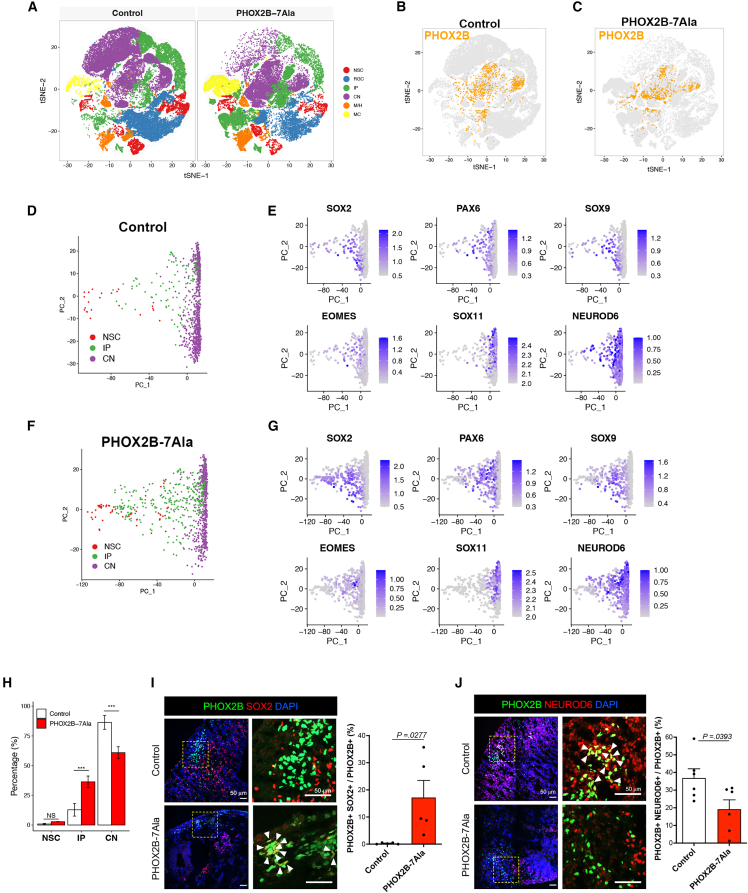
(A) t-SNE projection of all 72,800 individual cells from day-60 HCOs into six main cell types, colored by cell types. PHOX2B+ cells in (B) control and (C) PHOX2B-7Ala HCOs after imputation analysis.
(D) Trajectory constructed by PCA analysis shows the lineage progression of PHOX2B+ cells from NSC to IP and CN states in the control HCOs.
(E) Canonical markers expressed in PHOX2B+ cells at NSC, IP, and CN states in the control HCOs.
(F) Trajectory constructed by PCA analysis shows the lineage progression of PHOX2B+ cells from NSC to IP and CN states in the PHOX2B-7Ala HCOs.
(G) Canonical markers expressed in PHOX2B+ cells at NSC, IP, and CN states in the PHOX2B-7Ala HCOs.
(H) Barplot showing the population sizes of PHOX2B+ cells at NSC, IP, and CN states in the control and PHOX2B-7Ala HCOs (mean ± SEM). ∗∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001; NS, non-significant.
(I and J) Immunostaining of (I) PHOX2B+; SOX2+ and (J) PHOX2B+; NEUROD6+ cells in the control and PHOX2B-7Ala mutant HCOs as marked by the arrowheads. An enlargement of a square region in the image is shown in the right panel. Bar charts showing the quantitative data represented as mean ± SEM. n ≥ 3 per group from three independent experiments. Unpaired t test; two-sided. NSC, neural stem cells; RGC, radial glial cells; IP, intermediate progenitors; CN, cortical neurons; M/H, mid/hindbrain cells; MC, mesenchymal-like cells. See also Figures S5–S7 and Data S2.