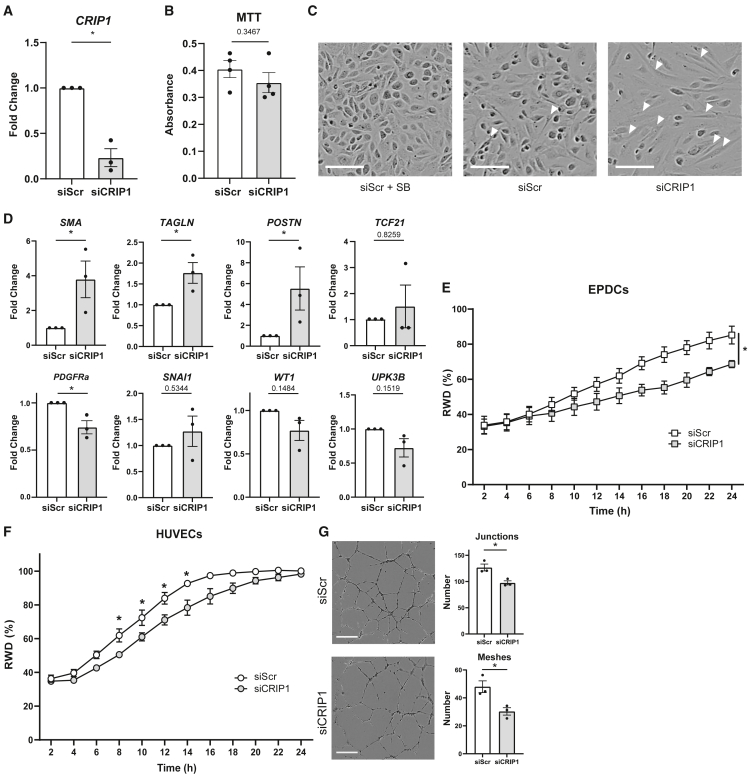
Figure 6.
siRNA-induced knockdown of CRIP1 induces EMT in an epicardial cell culture model
(A) Validation of knockdown using qPCR. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent samples. ∗p < 0.05; Student’s t test.
(B) MTT assay to assess proliferation in siScr and siCRIP1 treated cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of four independent samples.
(C) Representative images of primary epicardial cells after 48 h cultured with scrambled siRNA (siScr) and SB to maintain an epithelial phenotype, siSCR alone, or siCRIP1. Arrowheads indicate examples of mesenchymal cells. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(D) qPCR for mesenchymal markers (SMA, TAGLN, POSTN, TCF21, PDGFRa), EMT-related transcription factor SNAI1, and epithelium (UPK3B, WT1). Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent samples. ∗p < 0.05; Student’s t test.
(E) Wound healing assay in primary epicardial culture after knockdown of CRIP1. RWD: relative wound density, n = 3 independent samples, ∗p < 0.05 at 24 h. Student’s t test.
(F) Wound healing assay in HUVECs after knockdown of CRIP1, n = 3 independent samples. ∗p < 0.05; Student’s t test.
(G) Images of tube formation by HUVECs after knockdown of CRIP1. Right: number of junctions and meshes in HUVECs after 24 h. Scale bar: 400 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent samples. ∗p < 0.05; Student’s t test. See also Figure S5.