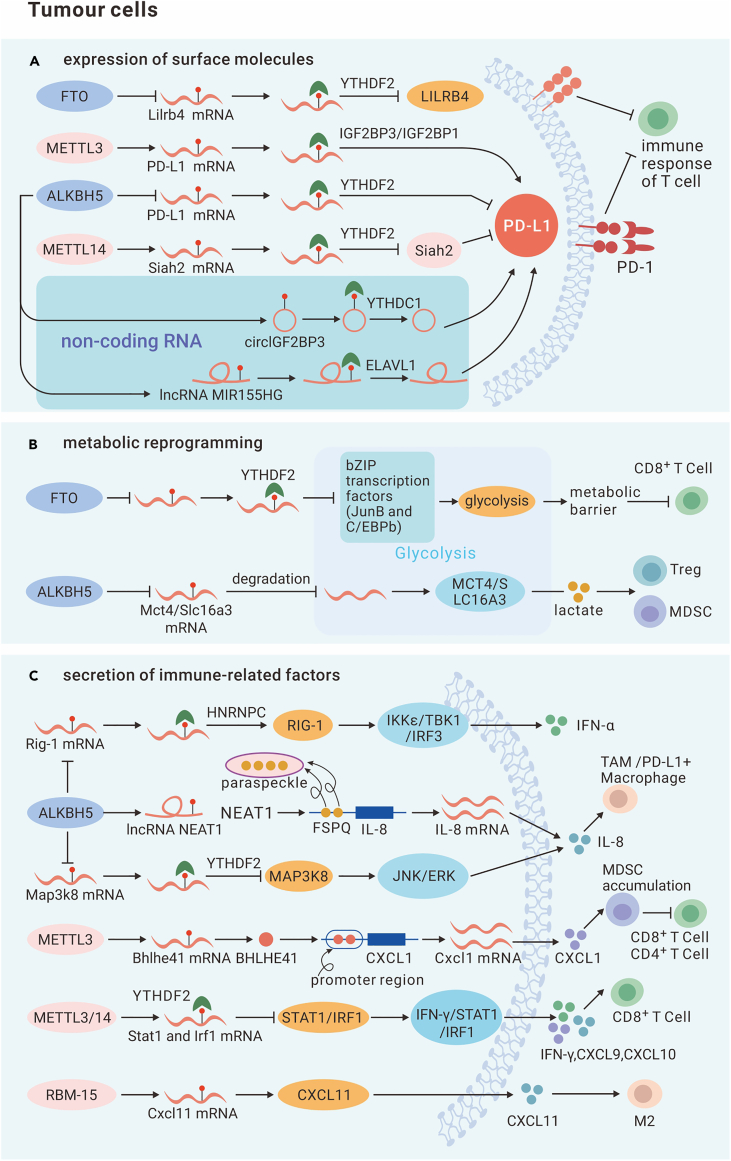
Figure 7.
The mechanisms by which m6A modification induces immune evasion in tumor cells
(A) FTO promotes ILIRB4 (an immune checkpoint) expression by targeting its mRNA. METTL3 and ALKBH5 upregulate the expression of PD-L1 by targeting PD-L1 mRNA, thus enhancing immunosuppression. METTL3 also regulates ncRNAs (circIGF2BP3 and lncMIR155HG). METTL14 negatively regulates Siah2 (a RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that enhances PD-L1 degradation) to increase PD-L1.
(B) FTO increases the metabolic barrier for T cell activation and inhibits the function of CD8+ T cells targeting JunB and C/EBPb (glycolysis regulators). ALKBH5 enhances lactate content in tumor-infiltrating Tregs and MDSCs by targeting Mct4/Slc16a3.
(C) ALKBH5 inhibits production of IFN-γ and IL-8 via the ALKBH5/RIG-I/IFNα axis, the ALKBH5/paraspeckle/CXCL8 axis, and the ALKBH5/MAP3K8 axis. METTL3 promotes CXCL1 production by targeting BHLHE4 (which binds to the promoter region of CXCL1) and induces immunosuppression. METTL3/14 also inhibits IFN-γ, CXCL9, and CXCL10 by inhibiting IFN-γ-STAT1-IRF1 signaling. RBM-15 promotes CXCL11 production, thus inducing M2 polarization.