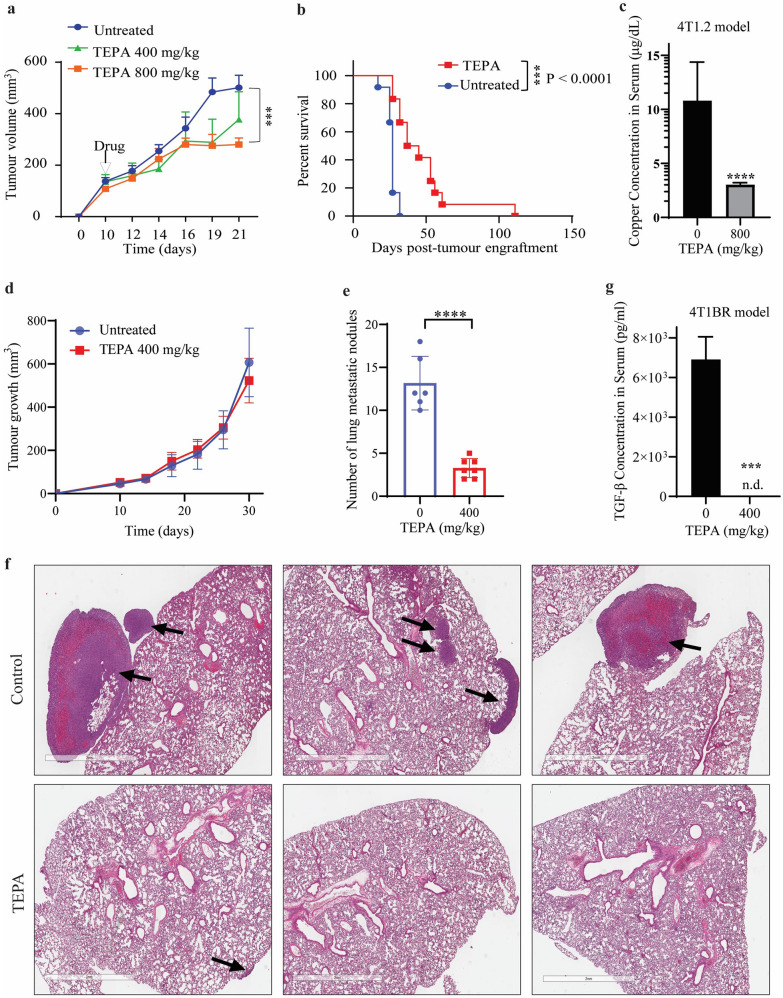
Fig. 1.
TEPA inhibits the in vivo tumor growth in a syngeneic model of triple-negative breast cancer. a Murine 4T1.2 syngeneic TNBC tumor growth following treatment with vehicle or TEPA (400 mg/kg and 800 mg/kg, daily, oral gavage) for three weeks is shown. Treatment was started once tumors became palpable (50–100 mm3). The mean tumor volume of each treatment group from each mouse is presented (n = 6 mice/group). Two-way ANOVA was followed by Sidak’s post-test for tumor growth analysis. b The survival analysis for murine 4T1.2 syngeneic TNBC tumors following treatment with vehicle or TEPA (800 mg/kg, daily, oral gavage) for three weeks is calculated by the Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. c Copper concentrations in 4T1.2 mice model sera treated with 800 mg/kg TEPA compared to the vehicle controls. Mice were treated with TEPA for three weeks, treatment was withdrawn, and mice were followed for survival until tumors reached 1000 mm3. Down, TEPA reduces lung metastases in 4T1BR metastatic TNBC model in vivo. Murine 4T1BR tumor-bearing mice were treated with vehicle or TEPA (400 mg/kg, daily, oral gavage) for three weeks. At the end of the treatment, lungs were isolated and stained with H&E to analyze tumor metastases. d Tumor growth analysis of murine 4T1BR tumor-bearing mice treated with vehicle or TEPA (400 mg/kg). Two-way ANOVA was followed by Sidak’s post-test for tumor growth analysis (n = 6). e Quantification of the number of metastatic lung nodules in the vehicle and TEPA-treated mice. Unpaired “t” test was performed (n = 6). f Representative images of lung metastasis in 4T1BR tumor model treated with the vehicle or TEPA. The metastatic nodules were stained with H&E. g The protein level of TGF-β in the sera of 4T1BR syngeneic mice treated with TEPA (400 mg/Kg, daily, oral gavage) for 30 days