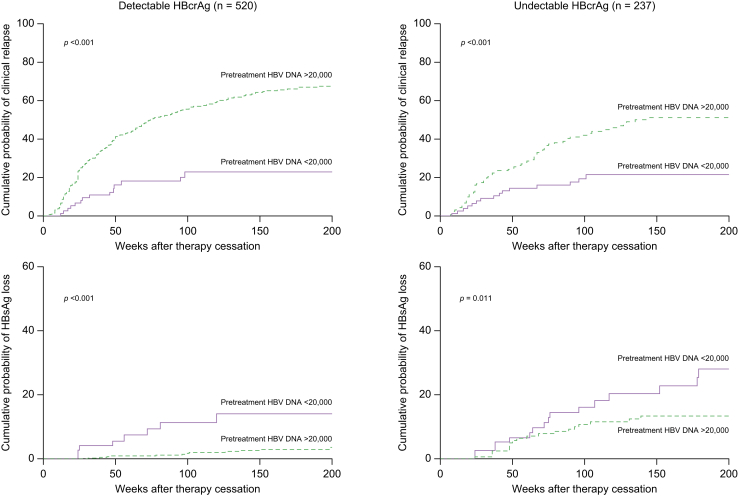
Fig. 3.
Off-treatment outcomes according to pretreatment HBV DNA levels stratified by end-of-treatment HBcrAg levels.
Cumulative probability of clinical relapse and HBsAg loss according to pre-treatment HBV DNA levels for patients with detectable (n = 520; 74 [14%] with pretreatment HBV DNA <20,000 IU/ml) and undetectable HBcrAg (n = 237; 76 [32%] with pretreatment HBV DNA <20,000 IU/ml) at the end of treatment. A pretreatment HBV DNA level <20,000 IU/ml was associated with a lower cumulative risk of clinical relapse (p <0.001 by log-rank test) and a higher cumulative chance of HBsAg loss (p <0.001 by log-rank test) among patients with detectable HBcrAg at the end of treatment; similar results were obtained among patients with undetectable HBcrAg at the end of treatment (p <0.001 for clinical relapse and p = 0.011 for HBsAg loss). HBcrAg, hepatitis B core-related antigen.