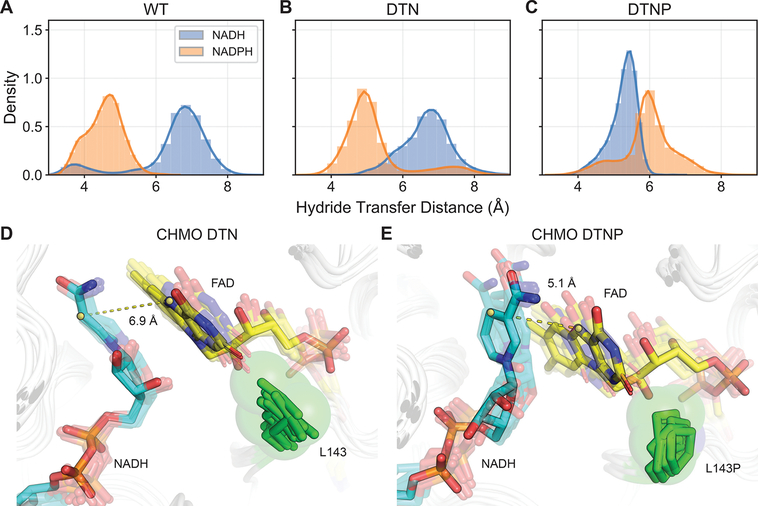
Figure 4.
Evaluation of hydride transfer efficiency in CHMO variants. Shorter distances between NAD(P)H C4 and FAD N5 contribute to enhanced catalysis. (A, B) WT and DTN are both marked by NADPH sampling distances ~5 Å, while the less active NADH samples distances are >6 Å and are too remote to engage in hydride transfer. (C) DTNP displays the opposite arrangement, with NADH sampling closer distances than NADPH. (D) L143 in DTN firmly packs under the flavin ring, blocking the flavin from moving closer to nicotinamide, resulting in suboptimal hydride transfer distance. (E) L143P presses against the FAD ribitol rather than contacting the flavin. This anchors the FAD core and allows the flavin head to rotate in response to changes in the nicotinamide positioning to sustain closer contact. The dashed lines show representative distances between the nicotinamide C4 and FAD N5.