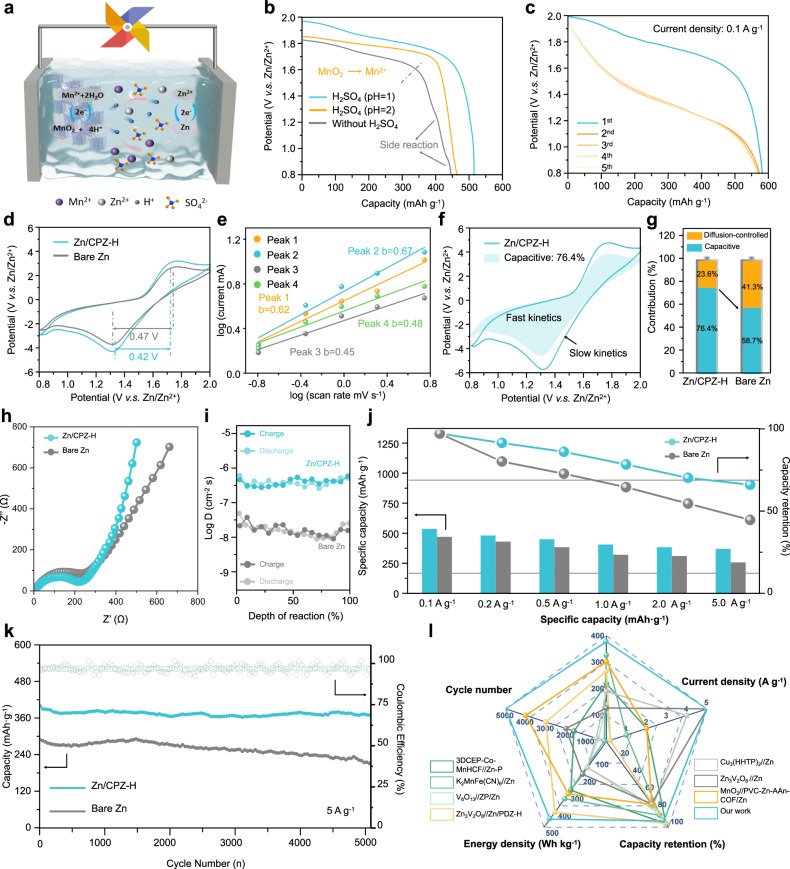
Fig. 4. Electrochemical performance and reaction mechanism of a Zn/CPZ-H//MnO2 full battery.
a Schematic illustration of reactions that occur in an aqueous-acid Zn/CPZ-H//MnO2 battery. b First discharge curves of Zn/MnO2 batteries containing the CPZ-H electrolyte and various concentrations of H+. c Discharging capacity of a cell in the first five cycles at a current density of 0.1 A g−1. d CV curves of Zn/CPZ-H//MnO2 and bare Zn//MnO2 full cells at a scan rate of 2 mV s−1. e Plots of corresponding log(i) versus log(v) curves of various peaks. f CV curve of Zn/CPZ-H//MnO2 full cell at 5 mV s−1 showing the contribution to the capacitance from fast kinetic processes and the slow kinetic processes. g Comparison of capacitance contributions in terms of h EIS curves and i Zn2+ diffusion coefficients (DZn2+) of Zn/CPZ-H//MnO2 and bare Zn//MnO2 full cells. j Rate performance and capacity retention and k long-term cycling performance at a current density of 5 A g−1 of Zn/CPZ-H//MnO2 full cell. l Comparison of the performance of the battery in the current study with the performances that have been reported for other Zn-ion batteries2,3,5,17,23–33.