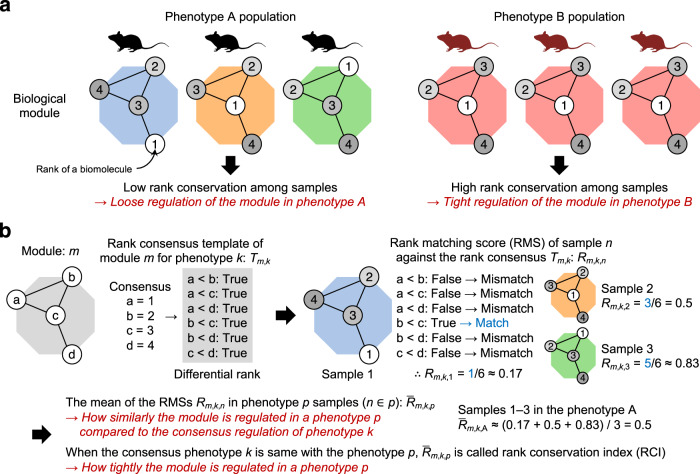
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of Differential Rank Conservation.
a The concept of rank conservation. A module of a biological system can be represented as a molecular network where nodes and edges indicate biomolecules (e.g., gene transcripts, proteins, and metabolites) and relationships (e.g., physical interactions, chemical reactions), respectively. For each sample, ranks of biomolecules can be obtained from experimental data by ordering the values of interest (e.g., abundances, levels of specific post-translational modification) between the biomolecules within a module. Low and high rank conservation among the samples within a phenotype population suggest loose and tight regulation of the module in the population, respectively. b Overview of Differential Rank Conservation (DIRAC) algorithm. DIRAC algorithm utilizes differential ranks of the pairwise rank comparisons within a biological module, and summarizes the rank patterns into sample-level rank matching score (RMS) and population-level rank conservation index (RCI).