Figure 4. Identification of novel ALK fusions in adult GBMs.
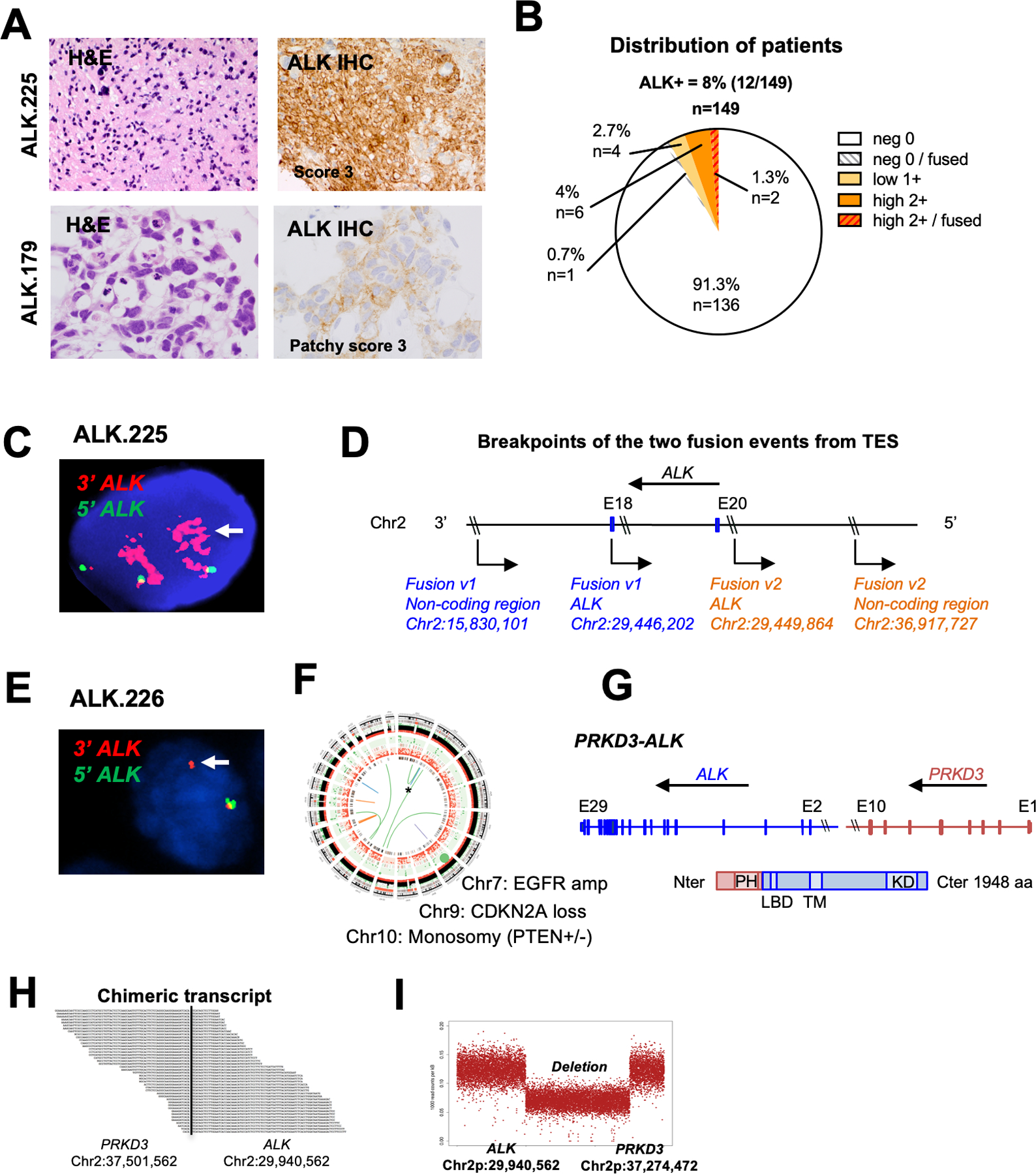
A. H&E staining and ALK IHC of two illustrative adult GBMs scored as IHC 3+ (left top) and 2+ (left bottom); Histology of tumor ALK.225 and ALK.179 showing hallmarks of glioma and strong ALK expression by IHC (score 3+) (ALK.225) and focal moderate staining (ALK.179).
B. Distribution of ALK IHC scores in the adult GBM cohort (n = 149).
C. ALK FISH of tumor ALK.225 showing rearrangement and amplification of the ALK 3’ region (red).
D. Schematic representation of the two ALK-noncoding genomic breakpoints. Fusion variant 1 (blue) occurred between ALK (in intron 20; breakpoint 2:29446202) and a non-coding genomic region on chromosome 2 (breakpoint 2:15830101). Fusion variant 2 (orange) occurred between ALK (exon 18; breakpoint 2:29449864) and a different non-coding region on chromosome 2 (breakpoint 2:36917727).
E. ALK FISH of tumor ALK.226 showing evidence of rearrangement (arrow, single 3’ red signal) and one normal appearing allele (yellow).
F. Circos plot of WGS for ALK.226 confirming novel PRKD3-ALK fusion co-occuring with classic adult GBM aberrations (EGFR amplification, CDKN2A loss, monosomy 10).
G. Schematic representation of the PRKD3-ALK variant, which fuses the N-terminal portion of PRKD3 (including the Pleckstrin homology domain PH implicated in protein membrane recruitment and intracellular trafficking) to the C-terminal portion of ALK starting with exon 2 (including the ligand binding domain LBD, transmembrane TM and kinase KD domains). Amino acid number is indicated on the right.
H. RNA sequencing of the PRKD3-ALK fusion demonstrates the novel breakpoints in intron 2 of ALK (chr2:29940562) and intron 10 of PRKD3 (chr2:37501562).
I. Copy number analysis shows a 7.5 MB interstitial deletion with breakpoints consistent with fusion of PRKD3 and ALK in-frame.
