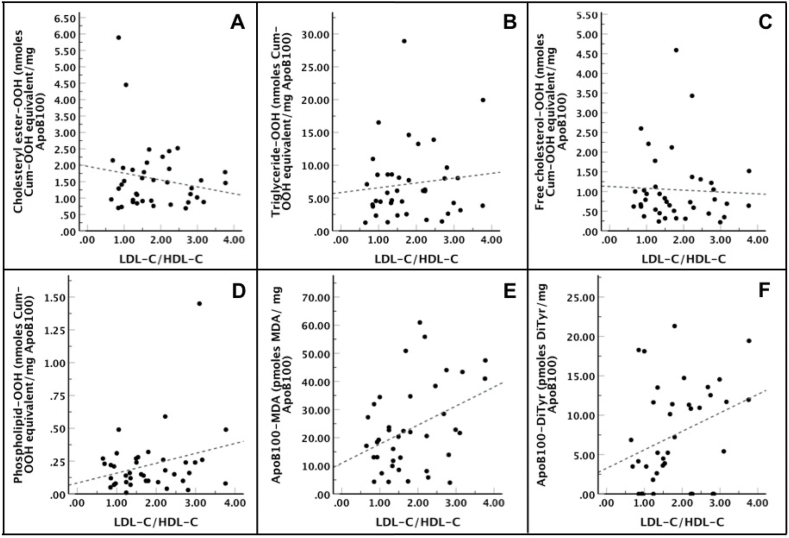
Fig. 4.
LDL-C/HDL-C ratio versus oxLDL markers in PD patients. The Linear Regression Analysis showed that: (i) cholesteryl ester-OOH [R2 = 0.01, F(1,37) = 1.20, β = −0.21, t = −1.10, p = 0.28] (panel A), triglyceride-OOH [R2 = 0.00, F(1,37) = 0.47, β = 0.73, t = 0.68, p = 0.50] (panel B), free cholesterol-OOH [R2 = 0.00, F(1,37) = 0.07, β = −0.05, t = −0.27, p = 0.79] (panel C) and phospholipid-OOH [R2 = 0.05, F(1,37) = 2.93, β = 0.08, t = 1.71, p = 0.10] (panel D) did not statistically correlate with LDL-C/HDL-C ratio. (ii) ApoB100-MDA [R2 = 0.12, F(1,37) = 6.31, β = 6.77, t = 2.51, p = 0.02] and apoB100-DiTyr [R2 = 0.08, F(1,37) = 4.18, β = 2.35, t = 2.04, p = 0.048] correlated proportionally and statistically with LDL-C/HDL-C ratio (panel E and F, respectively).