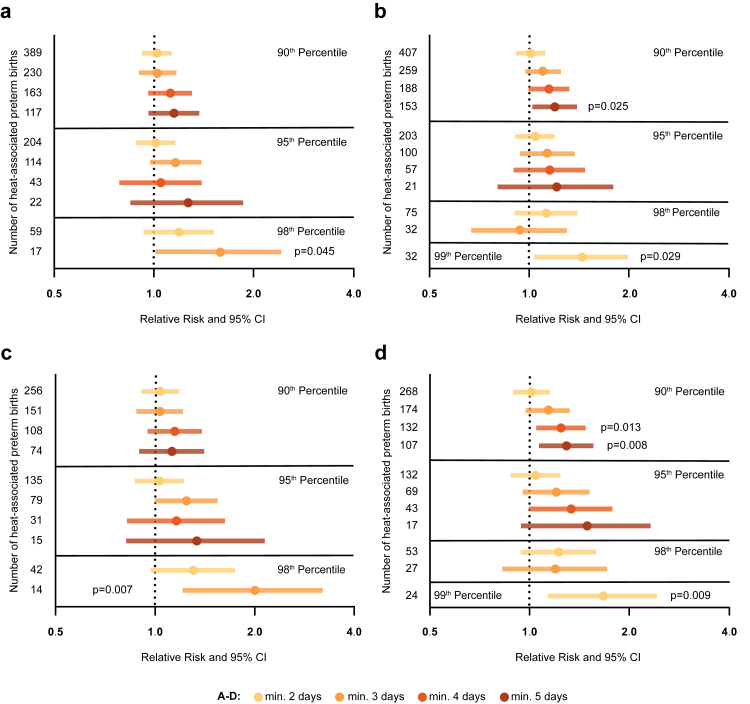
Fig. 2.
Periods of heat stress increase the relative risk of preterm birth, especially during gestation weeks 34–36 + 6 (late preterm birth). Relative risk of preterm delivery after heat exposure. Heat events are defined by the daily maximum temperature (a) or the daily apparent temperature (b) for all preterm births. Heat events defined by the daily maximum temperature (c) or the daily apparent temperature (d), stratified for late preterm births (n = 24,863). The number of preterm births per category is shown on the Y-axis; X-axis is displayed in log scale; RR, 95% CI; Pearson χ2.