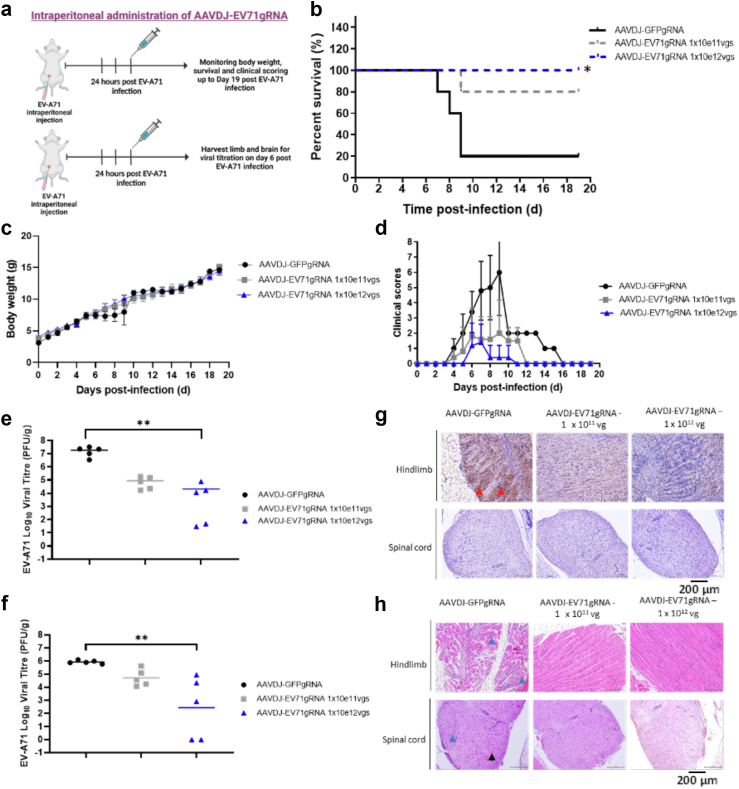
Fig. 4.
AAVDJ-CRISPR-CasRx prevents mortality and reduces pathology when applied 24 h after EV-A71 infection. a. BALB/c mice were injected intraperitoneally with a dose of 2 × 107 PFU EV-A71 per mouse at 5 days old. After 24 h, mice were injected intraperitoneally with a dose of 1 × 1011 viral genomes (vgs) or 1 × 1012 vgs of AAVDJ-EV71gRNAs per mouse. 1 × 1012 vgs AAVDJ-GFPgRNA was used as treatment control. b. The survival of the mice was recorded for 19 days post-infection (dpi). Comparison between two groups (CasRx-GFPg2 and CasRx-EV71_3Dguides) was analyzed by Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. ∗p < 0.05. c. The body weight of each mouse in each treatment group was recorded for 19 dpi. d. The clinical score of each mouse was recorded using the mice clinical assessment scoring system (M-CASS). e. Virus titers in the hind limbs of mice from different treatment groups were determined using the plaque-forming assay. Viral titration results were from a single experiment with multiple mice. f. Virus titers in the brains of mice from different treatment groups were determined using the plaque-forming assay. Comparison between two groups (CasRx-GFPg2 and CasRx-EV71_3Dguides) was analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparisons post hoc test. ∗∗p < 0.005. Viral titration results were from a single experiment with multiple mice. g. Immuno-histochemistry staining for EV-A71 specific antigen. Presence of viral antigen in the hind limbs (red arrow). h. H&E staining of the hind limbs and spinal cord of mice. Polymorphonuclear meningitis in the spinal cord (black arrow). Necrosis and focal interstitial mononuclear cell infiltrate in the hind limbs and spinal cord (blue arrow). Magnification of H&E and IHC images are taken at 200X.