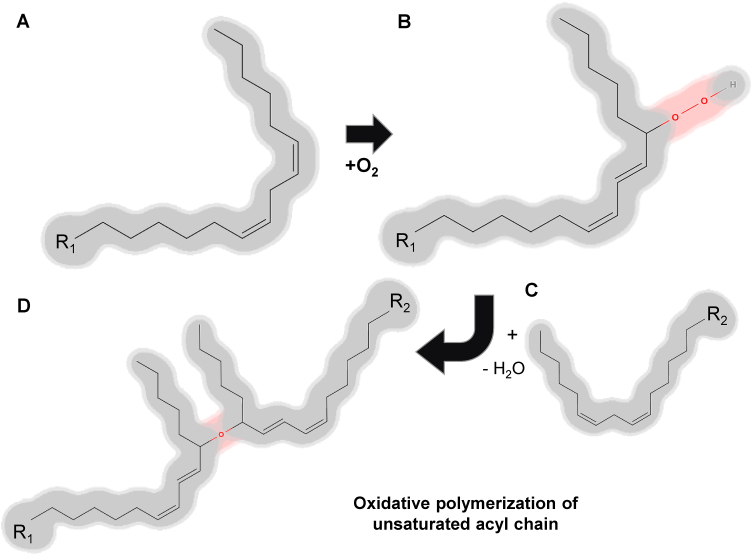
Fig. 2.
Oxidative polymerization of the unsaturated acyl chain. The oxidative polymerization of unsaturated fatty acids (A) is a consequence of autoxidation, which involves the addition of oxygen to the unsaturated fatty acyl chain (B) followed by subsequent crosslinking (C). Initially, an oxygen molecule is incorporated into carbon-hydrogen (C–H) bonds that are adjacent to one of the double bonds present within the unsaturated fatty acid (B). The resultant hydroperoxides are prone to undergo crosslinking reactions, whereby bonds are established between neighboring fatty acyl chains (C), leading to the formation of a polymer network (D).