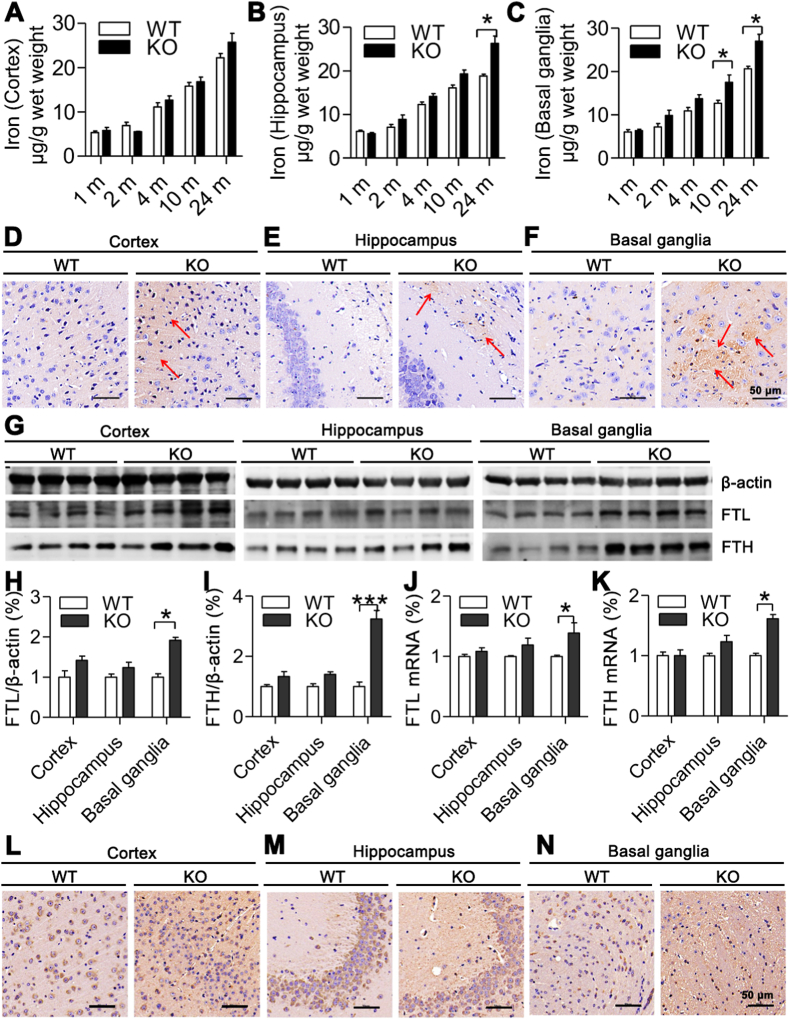
Fig. 1.
Effects of ApoE deficiency on iron content and expression of FTL and FTH in the cortex, hippocampus and basal ganglia of mice at different ages or at 24-months old.
A-C. Total iron contents (μg/g ww = wet weight) in the cortex (A), hippocampus (B) and basal ganglia (C) of ApoE−/− (n = 4) and WT (n = 4) mice at 1-, 2-, 4, 10, and 24-months old were measured by a GFAAS; D-F. DAB-enhanced Perls' iron staining of cortex, hippocampus and basal ganglia (Scale bar = 50 μm) of ApoE−/− (n = 4) and WT (n = 4) mice at age of 24-months old; G-I. Western blot analysis of FTL (G and H) and FTH (G and I) protein expression in ApoE−/− (n = 5) and WT (n = 3) mice; J and K. RT-PCR analysis of FTL (J) and FTH (K) mRNA expression in ApoE−/− (n = 4) and WT (n = 3) mice; L-N. Immunohistochemical examination of FTL protein expression in the cortex (L), hippocampus (M) and basal ganglia (N) of ApoE−/− (n = 4) and WT (n = 4) mice, Scale bar = 50 μm. Data were the mean ± SEM (% WT). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. WT mice.