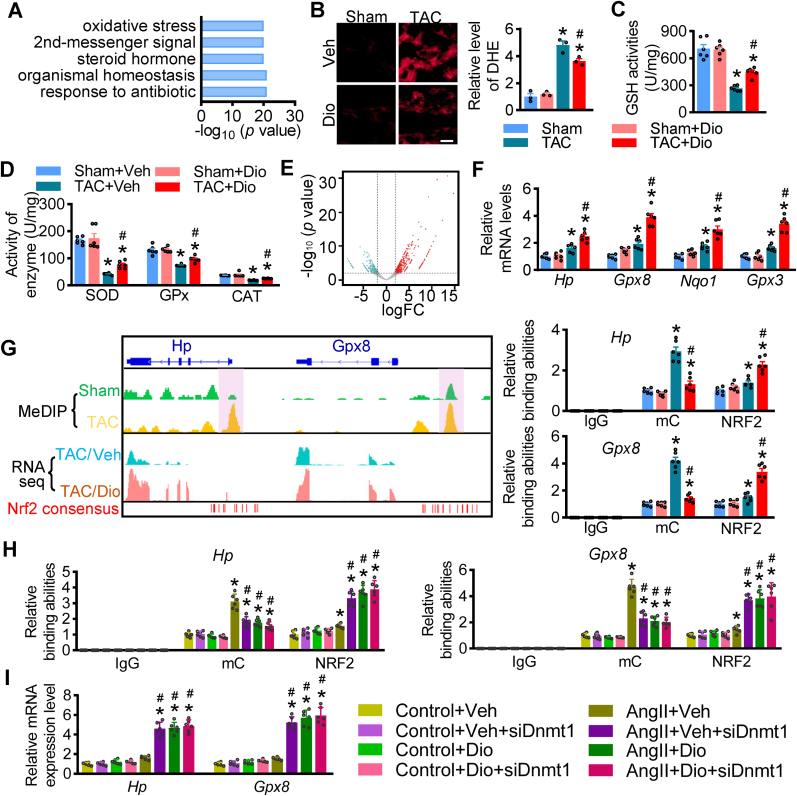
Fig. 4.
Dioscin alleviates oxidative stress via NRF2 transcriptional ability in hypertrophic hearts. (A) The gene ontology (GO) analysis of RNA-sequencing data using heart tissues from hypertrophic mice treated with dioscin. (B) Representative images of DHE staining in heart sections and its quantification (scale bar = 50 μm), n = 3 per group. (C) The measurement of GSH activity was performed using heart tissues from each group. (D) The enzymes activities of SOD, GPx and CAT were measured using heart tissues from mice. (E) The expression profile is presented in volcano map after RNAseq analysis. Compared with hearts from TAC mice, the up- (red) and down-regulated (blue) genes were indicated in hearts from TAC mice with dioscin administration. (F) qPCR assay is performed to detect the mRNA levels of some antioxidant genes up-regulated, including Hp, Gpx8, Nqo1 and Gpx3, after dioscin administration. (G) Left panel: Genome browser tracks displays DNA methylation levels, gene expression levels, differentially methylation regions (shaded vertical bars) and predicted NRF2-binding sites of Hp and Gpx8; right panel: ChIP-qPCR analysis is performed to detect the methylated levels and NRF2 binding abilities among the promoters of Hp and Gpx8 in heart tissues from mice using mC and NRF2 antibodies, respectively. IgG is considered as negative control (n = 6 per group, *P < 0.05 vs. Sham, #P < 0.05 vs. TAC). (H and I) AngII-incubated NMCMs were transfected with siRNA against Dnmt1 and then treated with dioscin. (H) ChIP-qPCR analysis was performed to detect the methylated levels and NRF2 binding abilities among the promoters of Hp and Gpx8 in NMCMs, respectively. (I) The mRNA expression of Hp and Gpx8 levels in AngII-cultured NMCMs after siDnmt1 transfection (n = 6 per group; *P < 0.05 vs. Control, #P < 0.05 vs. AngII + Veh, & P < 0.05 vs. AngII + Dio). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)